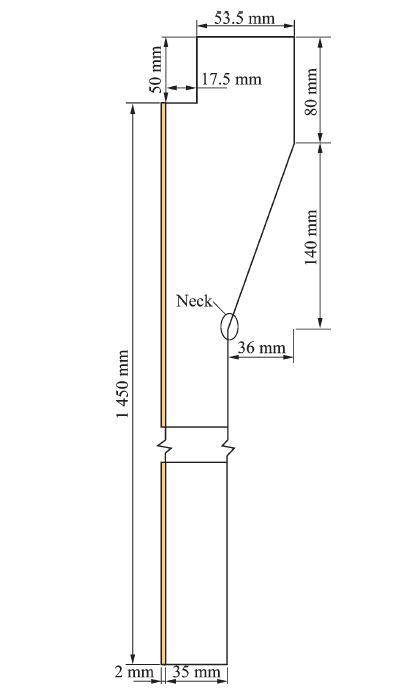
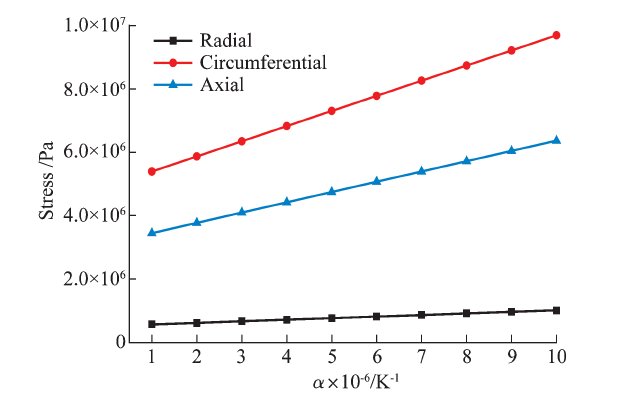
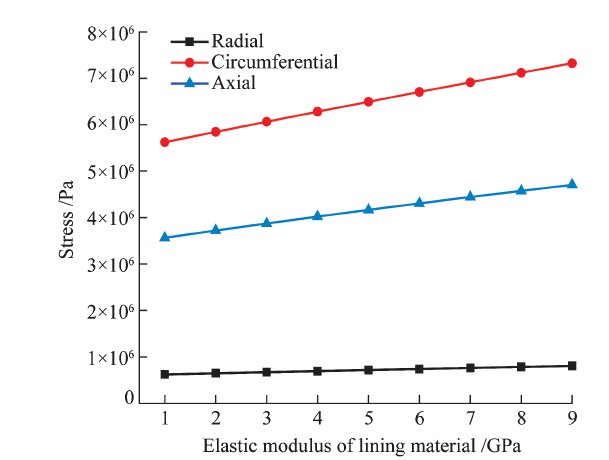
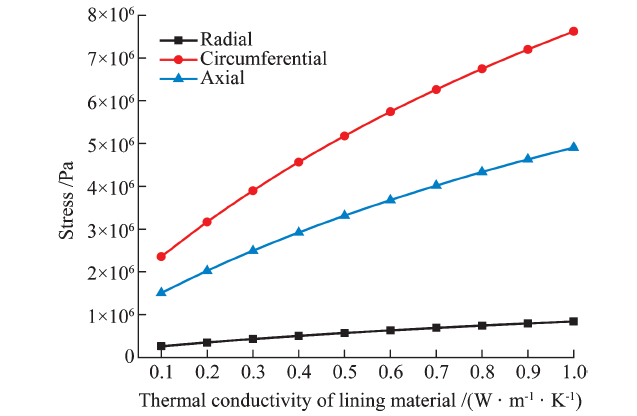
| [1] |
Yunpeng ZHOU, Wang FENG, Shankha CHATTERJEE, Andus BUHR, Sebastian KLAUS.
Study on Chrome-free Purging Plugs for Steel Ladles
[J]. China's Refractories, 2024, 33(2): 41-47.
|
| [2] |
GUO Peng, CHEN Lu, YU Tongshu, ZHANG Hui, WANG Dongdong.
Effect of Zirconia Corundum Addition on Properties of Chrome Corundum Castables
[J]. China's Refractories, 2023, 32(2): 41-44.
|
| [3] |
LI Yanjing, SUN Jialin, LI Yong, KANG Jian, MA Shulong, MA Fei, ZHANG Jili.
Influence of Flotation Magnesia Particles and Al2O3 Fines on Properties of Periclase-spinel Bricks
[J]. China's Refractories, 2022, 31(4): 12-15.
|
| [4] |
LIU Zhenglong, DENG Chengji, YU Chao, DING Jun, ZHU Hongxi.
Effect of C@SiC Composite Powder Addition on Properties of Al2O3-SiC-C Castables for Iron Trough
[J]. China's Refractories, 2022, 31(4): 39-44.
|
| [5] |
HAO Xian, LIU Guoqi, LI Zhixing, XU Chaojie, ZHANG Jianwei, LI Yong, LI Hongyu, LI Hongxia, FU Baoquan.
Effect of Al-Si Alloy Addition on Properties of Fused Spinel Carbon Materials
[J]. China's Refractories, 2022, 31(4): 45-52.
|
| [6] |
CAO Huiyan, FENG Yanbin, ZHANG Haiyan, MA Zhaoyang, LI Jie, WANG Xinhui, WU Jiguang, YANG Wengang.
Optimization and Simulation of Inclined Channel Area Lining for CDQ Ovens
[J]. China's Refractories, 2022, 31(2): 24-29.
|
| [7] |
ZHU Shaojun.
Damage Mechanism and Countermeasures of Al2O3-SiC-C Refractories Under Extreme Conditions
[J]. China's Refractories, 2022, 31(2): 7-11.
|
| [8] |
YAN Mingwei, LIU Kaiqi, ZHANG Jiayu, SUN Guangchao, LI Xiang, SI Kaikai.
Research Progress on Thermal Shock Behavior of Porous Ceramics
[J]. China's Refractories, 2022, 31(1): 24-29.
|
| [9] |
HAN Xiaoyuan, SHI Kai, XIA Yi, WANG Peixun, LIU Yang, SHANG Jianzhao.
Effects of Three Silicon-based Raw Materials on Properties and Microstructure of MgO-Al-C Materials
[J]. China's Refractories, 2021, 30(4): 30-35.
|
| [10] |
GUO Hongxiang, SUN Xiaogai, JIA Quanli, LI Xueyan, LIU Xinhong.
Effect of Calcium Chloride Addition on Properties of Corundum Spinel Castable
[J]. China's Refractories, 2020, 29(4): 46-49.
|
| [11] |
XIA Wenbin, ZHAN Huasheng, LI Jinyu, LI Yanjing, MA Shulong, SU Yuzhu, ZHANG Jili, GAO Changhe.
Effect of Andalusite Addition on Properties of Chrome-corundum Bricks
[J]. China's Refractories, 2020, 29(2): 21-24.
|
| [12] |
LAO Dong, JIA Wenbao, WANG Yufan, CHEN Ruoyu, LI Shujing, HEI Daqian, WANG Zhonghua, DING Yue, ZHANG Wenhao, LIU Meiqi.
Fabrication and Properties of Alumina-based Reticulated Porous Ceramics
[J]. China's Refractories, 2020, 29(2): 31-36.
|
| [13] |
HE Jian, LYU Xusheng, ZHANG Jialiang, ZHOU Wei, LI Yin.
Application Performance of Microporous Sintered Alumina in Alumina Magnesia Castables for Ladles
[J]. China's Refractories, 2020, 29(2): 6-10.
|
| [14] |
TIAN Xuekun, CHEN Anbang, LI Na, LIAO Guihua, DING Dafei, YE Guotian.
Effect of Andalusite Aggregate Pre-fired at Different Temperatures on Properties of Al2O3-SiC-C Castables
[J]. , 2019, 28(2): 41-45.
|
| [15] |
ZHANG Yaran, MA Beiyue, YU Jingyu, SU Chang, REN Xinming, QIAN Fan, LIU Guoqi, LI Hongxia, YU Jingkun.
Preparation of SiC Porous Ceramics by Crystalline Silicon Cutting Waste
[J]. , 2018, 27(4): 46-50.
|
 ), LI Hongxia, YANG Wengang, QIAN Fan, YU Jianbin, MA Weikui
), LI Hongxia, YANG Wengang, QIAN Fan, YU Jianbin, MA Weikui