China's Refractories ›› 2020, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (2): 31-36.DOI: 10.19691/j.cnki.1004-4493.2020.02.006
• Original article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Fabrication and Properties of Alumina-based Reticulated Porous Ceramics
LAO Dong1, JIA Wenbao1, WANG Yufan1, CHEN Ruoyu1, LI Shujing2, HEI Daqian1, WANG Zhonghua3, DING Yue1, ZHANG Wenhao1, LIU Meiqi1
- 1 Institute of Nuclear Analysis Technology, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics,Nanjing 211106, China
2 College of Materials and Metallurgy, Wuhan University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430081, China
3 Wuxi Chenguang Refractories Co., Ltd., Yixing 214221, China
-
Revised:2021-05-13Online:2020-06-15Published:2020-06-15 -
About author:Lao Dong, obtained his bachelor's degree from Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics in 2014. Now he is a PhD student in the College of Materials Science and Technology in the same university. He majors in materials science and engineering, and his main research direction is porous structural ceramic materials.
Cite this article
LAO Dong, JIA Wenbao, WANG Yufan, CHEN Ruoyu, LI Shujing, HEI Daqian, WANG Zhonghua, DING Yue, ZHANG Wenhao, LIU Meiqi. Fabrication and Properties of Alumina-based Reticulated Porous Ceramics[J]. China's Refractories, 2020, 29(2): 31-36.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.cnref.cn/EN/10.19691/j.cnki.1004-4493.2020.02.006
| Starting materials | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | SiO2 | R2O | CaO | MgO | TiO2 | LOI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AMA-40 | 99.6 | 0.05 | 0.09 | 0.25 | ||||
| Almatis alumina | 99.0 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.25 | ||||
| AMA-10 | 99.8 | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.05 | ||||
| Kaolin | 33.09 | 0.76 | 45.65 | 1.15 | 0.04 | 0.12 | 0.33 | 17.89 |
Table 1 Chemical composition of starting materials /mass%
| Starting materials | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | SiO2 | R2O | CaO | MgO | TiO2 | LOI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AMA-40 | 99.6 | 0.05 | 0.09 | 0.25 | ||||
| Almatis alumina | 99.0 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.25 | ||||
| AMA-10 | 99.8 | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.05 | ||||
| Kaolin | 33.09 | 0.76 | 45.65 | 1.15 | 0.04 | 0.12 | 0.33 | 17.89 |
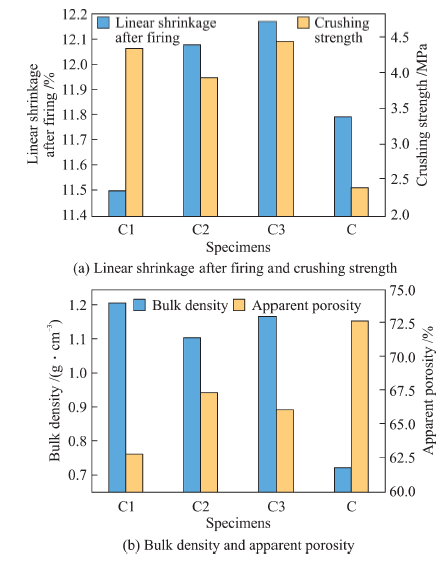
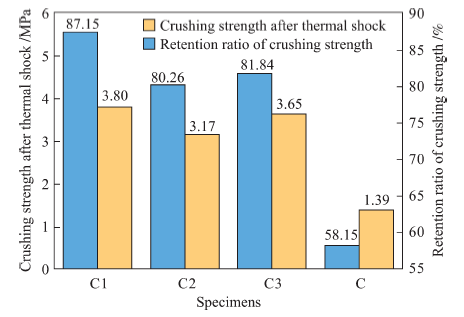
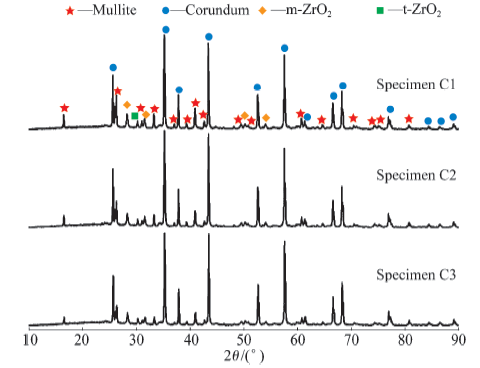
| Slurry No. | C1 | C2 | C3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| AMA-10 | 39 | 45 | 51 |
| Kaolin | 18 | 12 | 6 |
| Zirconia | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Deionized water | 40 | 40 | 40 |
| FS (extra adding) | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
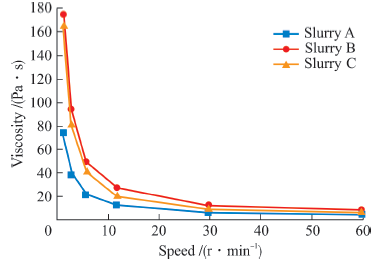
Table 2 Formulations of secondary impregnation slurry /mass%
| Slurry No. | C1 | C2 | C3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| AMA-10 | 39 | 45 | 51 |
| Kaolin | 18 | 12 | 6 |
| Zirconia | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Deionized water | 40 | 40 | 40 |
| FS (extra adding) | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| Items | C1 | C2 | C3 | Inner layer |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Modulus of elasticity / MPa | 212.03 | 230.57 | 258.58 | 230.57 |
| Poisson ratio | 0.32 | 0.32 | 0.32 | 0.32 |
| Thermal expansion coefficient×106 /K-1 | 7.5 | 8.1 | 8.6 | 8.1 |
Table 3 Performance parameters of secondary impregnation slurries
| Items | C1 | C2 | C3 | Inner layer |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Modulus of elasticity / MPa | 212.03 | 230.57 | 258.58 | 230.57 |
| Poisson ratio | 0.32 | 0.32 | 0.32 | 0.32 |
| Thermal expansion coefficient×106 /K-1 | 7.5 | 8.1 | 8.6 | 8.1 |
| [1] | Ren Xinming, Ma Beiyue, Zhang Yaran, Li Dongxu, Yu Jingkun, Liu Guoqi, Li Hongxia. Influence of calcining temperature on properties of SiC-Al2O3 porous ceramics prepared by polymeric replication method. Naihuo Cailiao (Refractories, in Chinese), 2018,52(3):196-198. |
| [2] | Bai Jiahai. Preparation and properties of porous SiC-cordierite ceramics. Naihuo Cailiao (Refractories, in Chinese), 2006,40(4):291-293. |
| [3] | Yin Yue, Ma Beiyue, Zhang Bowen, Li Shiming, Yu Jingkun. Latest development on research of oxide porous ceramics. Naihuo Cailiao (Refractories, in Chinese), 2016,50(5):393-400. |
| [4] | Chen Ruoyu, Hei Daqian, Wang Yufan, Zhou Qianbo, Liu Xinya, Xiao Qiqiao, Feng Yangchun, Jia Wenbao. Progress in preparation of porous structure ceramics by organic foam impregnation method. Naihuo Cailiao (Refractories, in Chinese), 2018,52(6):475-480. |
| [5] | Ahmad Hadi, Rahmatollah Emadi, Saeid Baghshahi, S. H. Naghavi. Different pore size alumina foams and study of their mechanical properties. Ceramics Silikaty, 2015,59(1):6-9. |
| [6] | Li Yuhai, Yu Fang, Gong Ganlei, Lyu Peng. Study on the preparation technics of ZrO2/Al2O3 multiphase foam ceramic. Foundry (in Chinese), 2007,56(10):1103-1106. |
| [7] | Xinwen Zhu, Dongliang Jiang, Shouhong Tan. Preparation of silicon carbide reticulated porous ceramics. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2002,23(1-2):232-238. |
| [8] |
J. Luyten, S. Mullens, J. Cooymans, A. M, De Wilde, I Thijs. New processing techniques of ceramic foams. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2003,5(10):715-718.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
U. F. Vogt, M Gorbar, P. Dimopoulos-Eggenschwiler, A. Broenstrup, G. Wagner, P. Colombo. Improving the properties of ceramic foams by a vacuum infiltration process. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2010,30(15):3005-3011.
DOI URL |
| [10] | Liu Yannian. Construction structure adhesive viscosity and thix-otropic experiment analysis. Sichuan Building Science (in Chinese), 2008,34(6):77-81. |
| [11] | Wang Yufan. Effect of the andalusite addition on the properties of fly ash based foam ceramics. Proceedings of the 16th China’s Refractories Youth Symposium, Dashiqiao, China, 2018. |
| [12] | Tobias Fey, Ulf Betke, Stefan Rannabauer, Michael Scheffler. Reticulated replica ceramic foams: processing, functionalization, and characterization. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2017,19(10):369-384. |
| [13] |
Xiong Liang, Yawei Li, Jun Liu, Shaobai Sang, Yuanyuan Chen, Benwen Li, Christos G. Aneziris. Improvement of the mechanical properties of SiC reticulated porous ceramics with optimized three-layered struts for porous media combustion. Ceramics International, 2017 43(4):3741-3747.
DOI URL |
| [1] | Burhanuddin, Harald HARMUTH. Effect of Slag Basicity on Alumina Dissolution and Diffusivity: A High-temperature Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy Study [J]. China's Refractories, 2024, 33(2): 27-34. |
| [2] | Yunpeng ZHOU, Wang FENG, Shankha CHATTERJEE, Andus BUHR, Sebastian KLAUS. Study on Chrome-free Purging Plugs for Steel Ladles [J]. China's Refractories, 2024, 33(2): 41-47. |
| [3] | Valeriy V. MARTYNENKO, Iryna G. SHULYK, Yuliya Ye. MISHNYOVA, Tetyana G. TYSHYNA. Investigation of Microstructure and Phase Composition of Chromic Oxide, AZS/Cr and High-alumina Refractories after Exposure of Basalt and Aluminaboronsilicate Glasses Melts [J]. China's Refractories, 2024, 33(1): 1-6. |
| [4] | DU Juan, GUO Huishi, YANG Jialin, LI Wenfeng, GUI Yanghai, ZHAO Zhiqiang, LIU Yingfan. Effects of Al2O3-SiO2 Raw Material Types on Properties of Anorthite Based Insulation Refractories [J]. China's Refractories, 2024, 33(1): 23-27. |
| [5] | WANG Jia, SUN Xiaofei, XU Jianfeng, XU Peipei. Effects of Different Raw Materials and Additions on Wave Transparency of Alumina Fiber Products [J]. China's Refractories, 2024, 33(1): 40-43. |
| [6] | WANG Li, LIU Shijie, WEI Haoyu, MA Juanjuan, DONG Binbin, GENG Shangrui, YAN Miaoxin, QIN Feng, GUO Yusen. Aluminum and Activated Alumina Powder Additions on Microwave Synthesis of Al4SiC4 [J]. China's Refractories, 2024, 33(1): 44-48. |
| [7] | LIU Chenchen, HUANG Ao, NIE Jianhua, GU Huazhi, QIN Chuanjiang, Lidah Mpoli NACHILIMA. Corrosion Mechanism of Alumina-magnesia Dry Materials for Smelting Manganese/chromium Steel in Coreless Medium Frequency Induction Furnaces [J]. China's Refractories, 2023, 32(4): 8-15. |
| [8] | LEE Yaotsung, ZHAO Lite, LEE Johnson, LIU William. Analysis of Corrosion Mechanisms of Low-cement or No-cement Al2O3-MgO Gunning Mix with Special Calcined Alumina in Rotary Slag Test [J]. China's Refractories, 2023, 32(4): 16-21. |
| [9] | ZHANG Yifan, WANG Gang, WANG Qu, LU Keke, ZHANG Qi. Effect of ZrO2 Addition on Lanthanum Aluminate-based High Emissivity Coating Materials [J]. China's Refractories, 2023, 32(4): 38-41. |
| [10] | ZHOU Lianzhuo, WANG Zhoufu, WANG Xitang, LIU Hao, MA Yan, QUAN Zhenghuang. Effect of Al Powder and Si Powder Additions on Structure and Properties of Unburned Magnesium Aluminate Spinel Refractories [J]. China's Refractories, 2023, 32(3): 14-19. |
| [11] | ZAN Wenyu, MA Beiyue. Preparation of Lightweight Alumina-silica Castables by Replacing Closed-cell Perlite Aggregates with Coal Gangue Ceramsites [J]. China's Refractories, 2023, 32(3): 20-25. |
| [12] | FAN Muxu, HOU Xiaojing, FENG Zhiyuan, WANG Han, LIU Pengcheng, SHI Gan. Alkali Vapor Corrosion of Different Refractories at High Temperatures [J]. China's Refractories, 2023, 32(2): 24-30. |
| [13] | CAO Zhuang, JIA Qingwei, ZHANG Jun, ZHOU Huijun, LI Jinfeng, HUN Xianlei, YAN Leixin, QIN Hongbin, ZHANG Sanhua. Effect of Different Silica Fumes on Properties of Al2O3-SiC-C Castables for Iron Trough [J]. China's Refractories, 2023, 32(2): 31-36. |
| [14] | GUO Peng, CHEN Lu, YU Tongshu, ZHANG Hui, WANG Dongdong. Effect of Zirconia Corundum Addition on Properties of Chrome Corundum Castables [J]. China's Refractories, 2023, 32(2): 41-44. |
| [15] | XU Guotao, ZHAO Yuan, WU Jie, ZHANG Honglei, LIU Li, ZHANG Yanwen, ZHOU Wangzhi. Discussion on Abnormal Corrosion and Material Selection of Hot Iron Ladles with Steel Scrap Addition [J]. China's Refractories, 2023, 32(1): 1-5. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||