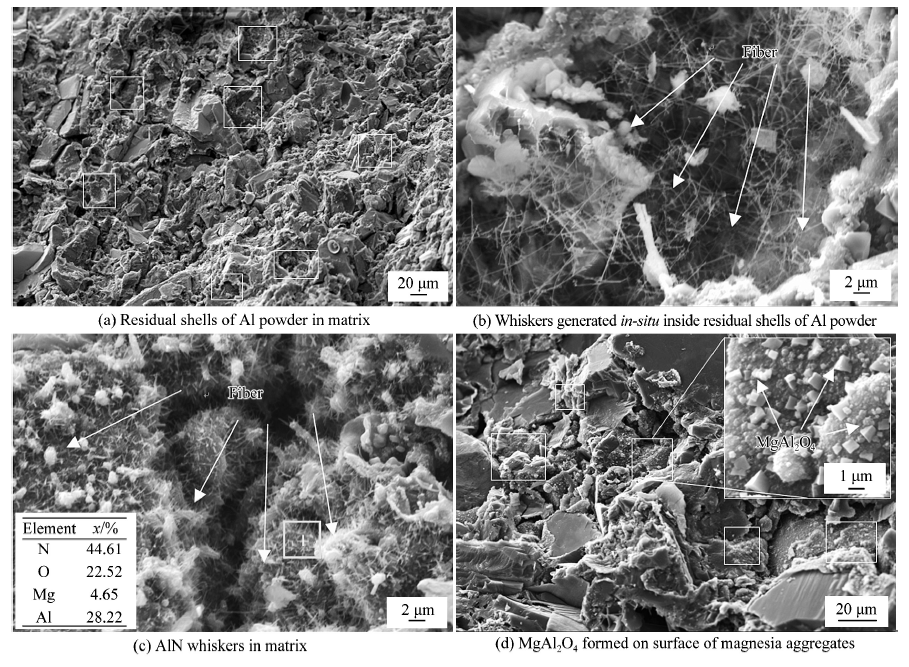
China's Refractories ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (4): 30-35.DOI: 10.19691/j.cnki.1004-4493.2021.04.006
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of Three Silicon-based Raw Materials on Properties and Microstructure of MgO-Al-C Materials
HAN Xiaoyuan, SHI Kai, XIA Yi, WANG Peixun, LIU Yang, SHANG Jianzhao
- School of Materials Science and Engineering, Henan University of Technology, Zhengzhou 450001, China
-
Online:2021-12-15Published:2021-12-10 -
About author:Han Xiaoyuan, born in 1995, is studying for her master’s degree in the School of Materials Science and Engineering, Henan University of Technology. Her main research field is MgO-C materials.
Cite this article
HAN Xiaoyuan, SHI Kai, XIA Yi, WANG Peixun, LIU Yang, SHANG Jianzhao. Effects of Three Silicon-based Raw Materials on Properties and Microstructure of MgO-Al-C Materials[J]. China's Refractories, 2021, 30(4): 30-35.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.cnref.cn/EN/10.19691/j.cnki.1004-4493.2021.04.006
| Raw materials | S0 | S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | S7 | S8 | S9 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 98 sintered magnesia | 3-1 mm | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| 98 fused magnesia | 1-0 mm | 15 | 13 | 11 | 9 | 13 | 11 | 9 | 10 | 5 | 0 |
| ≤0.074 mm | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | |
| Si | 0.5-0.2 mm | 0 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Fused quartz | 0.4-0.2 mm | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| SiC | 1-0 mm | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 10 | 15 |
| Al powder | ≤0.045 mm | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| Carbon black N220 | 25-20 nm | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Thermoset phenolic resin (extra adding) | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | |
Table 1 Formulations of samples /mass%
| Raw materials | S0 | S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | S7 | S8 | S9 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 98 sintered magnesia | 3-1 mm | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| 98 fused magnesia | 1-0 mm | 15 | 13 | 11 | 9 | 13 | 11 | 9 | 10 | 5 | 0 |
| ≤0.074 mm | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | |
| Si | 0.5-0.2 mm | 0 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Fused quartz | 0.4-0.2 mm | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| SiC | 1-0 mm | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 10 | 15 |
| Al powder | ≤0.045 mm | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| Carbon black N220 | 25-20 nm | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Thermoset phenolic resin (extra adding) | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | |
| Samples | S0 | S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | S7 | S8 | S9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
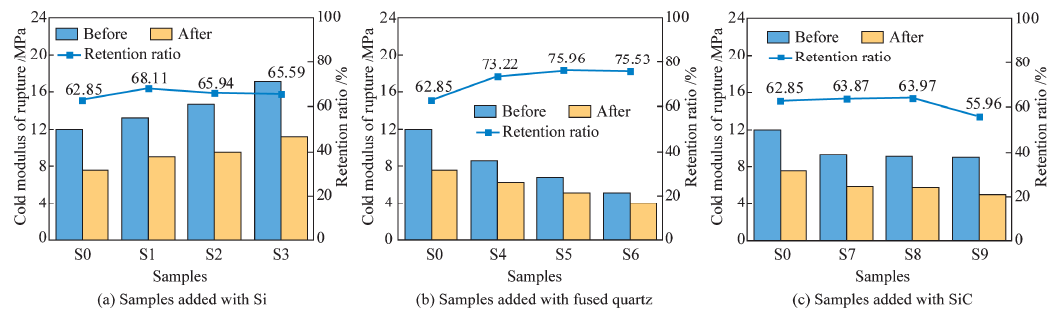
| CMOR | 14.5 | 17.3 | 15.9 | 16.1 | 14.6 | 13.4 | 12.9 | 14.7 | 19.1 | 17.9 |
| HMOR | 26.5 | 30.6 | 30.3 | 31.0 | 27.9 | 20.6 | 18.3 | 29.2 | 27.9 | 28.2 |
Table 2 Modulus of rupture of samples /MPa
| Samples | S0 | S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | S7 | S8 | S9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CMOR | 14.5 | 17.3 | 15.9 | 16.1 | 14.6 | 13.4 | 12.9 | 14.7 | 19.1 | 17.9 |
| HMOR | 26.5 | 30.6 | 30.3 | 31.0 | 27.9 | 20.6 | 18.3 | 29.2 | 27.9 | 28.2 |
| Samples | S0 | S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | S7 | S8 | S9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thickness of oxidation layer /mm | 1.71 | 1.70 | 1.66 | 1.58 | 1.76 | 2.12 | 2.38 | 1.68 | 1.60 | 1.62 |
Table 3 Oxidation resistance of samples
| Samples | S0 | S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | S7 | S8 | S9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thickness of oxidation layer /mm | 1.71 | 1.70 | 1.66 | 1.58 | 1.76 | 2.12 | 2.38 | 1.68 | 1.60 | 1.62 |
| [1] | Shi Kai, Xia Yi. Evolution of material systems of slide gates for steelmaking. Naihuo Cailiao (Refractories, in Chinese), 2018,52(3):230-236. |
| [2] | Yang Wengang, Li Hongxia, Liu Guoqi, Ma Tianfei, Qian Fan, Yu Jianbin. Structure design of SEN for high efficiency thin slab continuous casting. Naihuo Cailiao (Refractories, in Chinese), 2015,49(5):332-334, 338. |
| [3] | Shi Kai, Zhong Xiangchong. Properties and application of Al-Si metal bonded Al2O3-C slide plate. Naihuo Cailiao (Refractories, in Chinese), 2007,41(3):205-207, 219. |
| [4] | Shantanu K Behera. Bhagirath Mishra. Strengthening of Al2O3-C slide gate plate refractories with expanded graphite. Ceramics International, 2015,41(3):4254-4259. |
| [5] | Wang Heng, Li Yawei, Zhu Tianbin, Fu Zhengyi. Strengthening of Al2O3-C slide gate plate refractories with microcrystalline graphite. Ceramics International, 2017,43(13):9912-9918. |
| [6] | Li Shuxin, Duan Feng, Ren Xuehua, Ma Aiqiong, Li Bin. Research status and outlook of Al2O3-C slide gates for continuous casting. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2019,38(9):2847-2854, 2864. |
| [7] | Jinjin Ban, Chaojie Zhou, Long Feng, Quanli Jia, Xinhong Liu, Junhua Hu. Preparation and application of ZrB2-SiCw composite powder for corrosion resistance improvement in Al2O3-ZrO2-C slide plate materials. Ceramics International, 2020,46(7):9817-9825. |
| [8] | Jin Congjin, Li Zeya. Performance and use of alumina zirconia carbon slide plate for Baosteel ladle. Naihuo Cailiao (Refractories, in Chinese), 2004,38(5):359-360. |
| [9] | Wang Zihao, Zhang Jing, Wang Zhen, Ling Yongyi, Gao Jinxing, Liu Xinhong. Research progress of Al2O3-ZrO2-C slide plate material. Naihuo Cailiao (Refractories, in Chinese), 2021,55(3):264-271, 276. |
| [10] | Yao Jinfu, Shen Zhongming, Jin Congjin. Corrosion analysis of calcium treated steel on submerged nozzle. Naihuo Cailiao (Refractories, in Chinese), 2014,48(5):377-378. |
| [11] | Zhou Chunquan, Hang Guangzhen. Calcium treatment of molten steel and its corrosion to slide plates. Steelmaking (in Chinese), 1999(6):34-37. |
| [12] | Wang Fucheng. Production of magnesia slide gates for sliding nozzles. Foreign Refractories (in Chinese), 1994(9):38-41. |
| [13] | Wang Cheng, Zhang Wei, Zhang Shujun. Development of magnesia spinel slide plates. Naihuo Cailiao (Refractories, in Chinese), 1998(5):283-284. |
| [14] | Wei Zhongxian, Li Baoying, You Peiyu, Han Haiyan, Li Li. Development and application of fired magnesia spinel slide plate. Naihuo Cailiao (Refractories, in Chinese), 2002,36(4):229-230. |
| [15] | Wei Zhongxian, Ouyang Benhui. Development and application of magnesia-based composite slide plate. Naihuo Cailiao (Refractories, in Chinese), 2001,35(4):210-212. |
| [16] | Qiang Gu, Guoqi Liu, Hongxia Li, Quanli Jia, Fei Zhao, Xinhong Liu. Synthesis of MgO-MgAl2O4 refractory aggregates for application in MgO-C slide plate. Ceramics International, 2019,45(15):24768-24776. |
| [17] | Wei Zhongxian, Han Xiangming, Huang Tianjie, Luo Yan, Luo Deping. Development of aluminum bonded magnesia-spinel-carbon slide plate. Naihuo Cailiao (Refractories, in Chinese), 2007,41(6):457-459, 464. |
| [18] | Qu Jindong, Wei Heyi, Shi Deman, Gu Xiaohua. Study and application of magnesium aluminum carbon slide gate for steel ladle. Refractories & Lime (in Chinese), 2020,45(2):17-19. |
| [19] | Ma Teng, Liu Xinhong, Zhu Xiaoyan, Feng Long. Progress in research and application of Al-Si composite slide plates. Naihuo Cailiao (Refractories, in Chinese), 2014,48(3):231-235. |
| [20] | Liu Xinhong, Zhong Xiangchong. High temperature mechanical properties of Al and Si incorporated low carbon Al2O3-C slide plate materials. Naihuo Cailiao (Refractories, in Chinese), 2013,47(1):6-9. |
| [21] | Han Bingqiang, Dai Gang, Li Nan. Effects of fused quartz on properties of Al2O3-SiC-C Castable. Industrial Furnace, 2006,4(5):33-35. |
| [22] | Yan Guangzhou, Qian Fan, Yang Wenguang, Liu Guoqi. Effects of additives on properties of MgO-C nozzles. Naihuo Cailiao (Refractories, in Chinese), 2018,52(2):136-139. |
| [23] | Mao Xuesong, Gu Huazhi, Wang Houzhi. The effect of fused silica addition on thermal shock resistance of MgO material. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering (in Chinese), 2007,4(S2):358-361. |
| [1] | Yunpeng ZHOU, Wang FENG, Shankha CHATTERJEE, Andus BUHR, Sebastian KLAUS. Study on Chrome-free Purging Plugs for Steel Ladles [J]. China's Refractories, 2024, 33(2): 41-47. |
| [2] | LYU Chunjiang, CHANG Cheng, HUANG Yifei, CAO Huiyan, LI Jie, ZHU Chong. Preparation and Properties of SiC Assembled Large Block for Blast Furnace Tuyeres [J]. China's Refractories, 2023, 32(4): 1-7. |
| [3] | CHEN Yang, DENG Chengji, DING Jun, YU Chao, LOU Xiaoming. Effect of Ferric Nitrate Loading Mode on Properties of Si3N4 Composite MgO-C Refractories Prepared by Nitridation [J]. China's Refractories, 2023, 32(3): 6-9. |
| [4] | ZHOU Lianzhuo, WANG Zhoufu, WANG Xitang, LIU Hao, MA Yan, QUAN Zhenghuang. Effect of Al Powder and Si Powder Additions on Structure and Properties of Unburned Magnesium Aluminate Spinel Refractories [J]. China's Refractories, 2023, 32(3): 14-19. |
| [5] | CAO Huiyan, FENG Yanbin, ZHANG Xinhua, HUANG Zhigang, LI Jie, WANG Xinhui, WU Jiguang. Development and Application of Multi-phase Nitrides Bonded Silicon Carbide Lintel Blocks for Dry Quenching Furnaces [J]. China's Refractories, 2023, 32(2): 7-11. |
| [6] | WANG Jiaping, WU Jiguang, HUANG Zhigang, LYU Chunjiang, WANG Wenwu. Steam Oxidation Resistance Comparison of Several Silicon Carbide Refractories at Elevated Temperatures [J]. China's Refractories, 2023, 32(2): 18-23. |
| [7] | CAO Zhuang, JIA Qingwei, ZHANG Jun, ZHOU Huijun, LI Jinfeng, HUN Xianlei, YAN Leixin, QIN Hongbin, ZHANG Sanhua. Effect of Different Silica Fumes on Properties of Al2O3-SiC-C Castables for Iron Trough [J]. China's Refractories, 2023, 32(2): 31-36. |
| [8] | GUO Peng, CHEN Lu, YU Tongshu, ZHANG Hui, WANG Dongdong. Effect of Zirconia Corundum Addition on Properties of Chrome Corundum Castables [J]. China's Refractories, 2023, 32(2): 41-44. |
| [9] | GU Chenwei, WANG Zhanmin, ZHAO Shixian, SI Yaochen, XIA Miao. Formation of Polytypoids (12H and 21R) in High Temperature Nitrogen Atmosphere and Their Effects on SiC-MgAl2O4 Composites [J]. China's Refractories, 2023, 32(2): 45-50. |
| [10] | XU Guotao, ZHAO Yuan, WU Jie, ZHANG Honglei, LIU Li, ZHANG Yanwen, ZHOU Wangzhi. Discussion on Abnormal Corrosion and Material Selection of Hot Iron Ladles with Steel Scrap Addition [J]. China's Refractories, 2023, 32(1): 1-5. |
| [11] | TIAN Xuekun, ZHOU Chaojie, ZHANG Lei, ZHAO Fei, JIA Quanli, LIU Xinhong, ZHONG Xiangchong. Preparation of ZrB2-ZrO2-SiC Composite Powder by Carbothermal Reduction from Zircon [J]. China's Refractories, 2023, 32(1): 25-29. |
| [12] | LI Yanjing, SUN Jialin, LI Yong, KANG Jian, MA Shulong, MA Fei, ZHANG Jili. Influence of Flotation Magnesia Particles and Al2O3 Fines on Properties of Periclase-spinel Bricks [J]. China's Refractories, 2022, 31(4): 12-15. |
| [13] | LIU Zhenglong, DENG Chengji, YU Chao, DING Jun, ZHU Hongxi. Effect of C@SiC Composite Powder Addition on Properties of Al2O3-SiC-C Castables for Iron Trough [J]. China's Refractories, 2022, 31(4): 39-44. |
| [14] | HAO Xian, LIU Guoqi, LI Zhixing, XU Chaojie, ZHANG Jianwei, LI Yong, LI Hongyu, LI Hongxia, FU Baoquan. Effect of Al-Si Alloy Addition on Properties of Fused Spinel Carbon Materials [J]. China's Refractories, 2022, 31(4): 45-52. |
| [15] | Valeriy V. MARTYNENKO, Vladimir V. PRIMACHENKO, Pavlo O. KUSHCHENKO, Irina G. SHULIK, Ludmyla K. SAVINA. Effects of a Combined Silica-containing Additive on Structural and Rheological Properties of a Low-cement Silicon Carbide Castable [J]. China's Refractories, 2022, 31(2): 1-6. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||