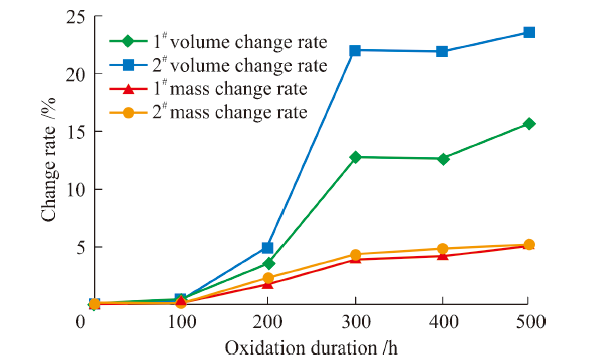
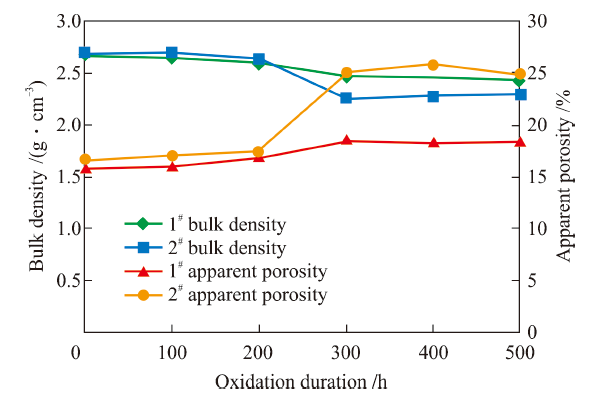
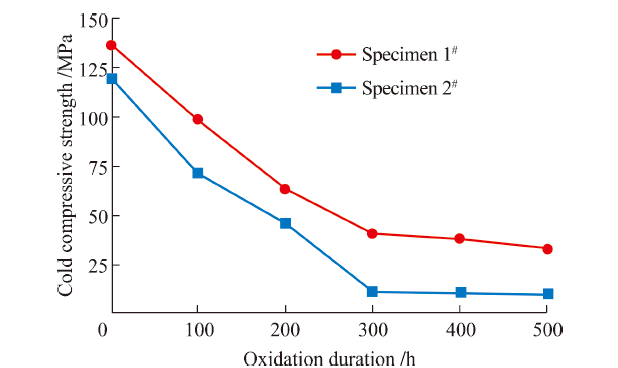
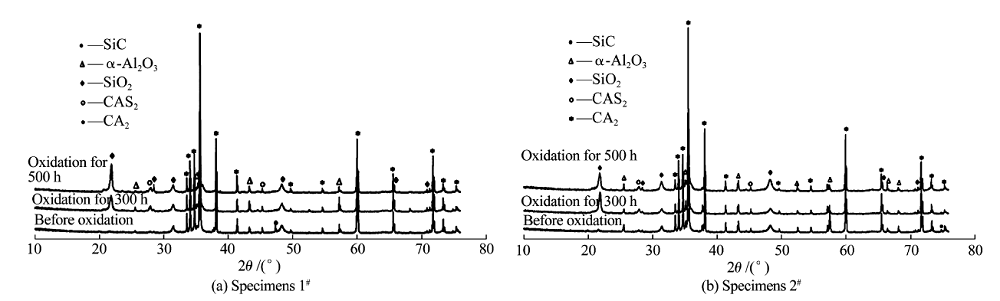
China's Refractories ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (3): 23-27.DOI: 10.19691/j.cnki.1004-4493.2021.03.005
Previous Articles Next Articles
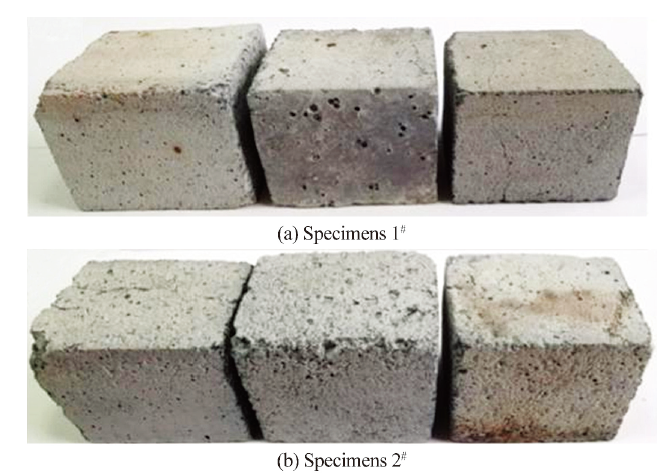
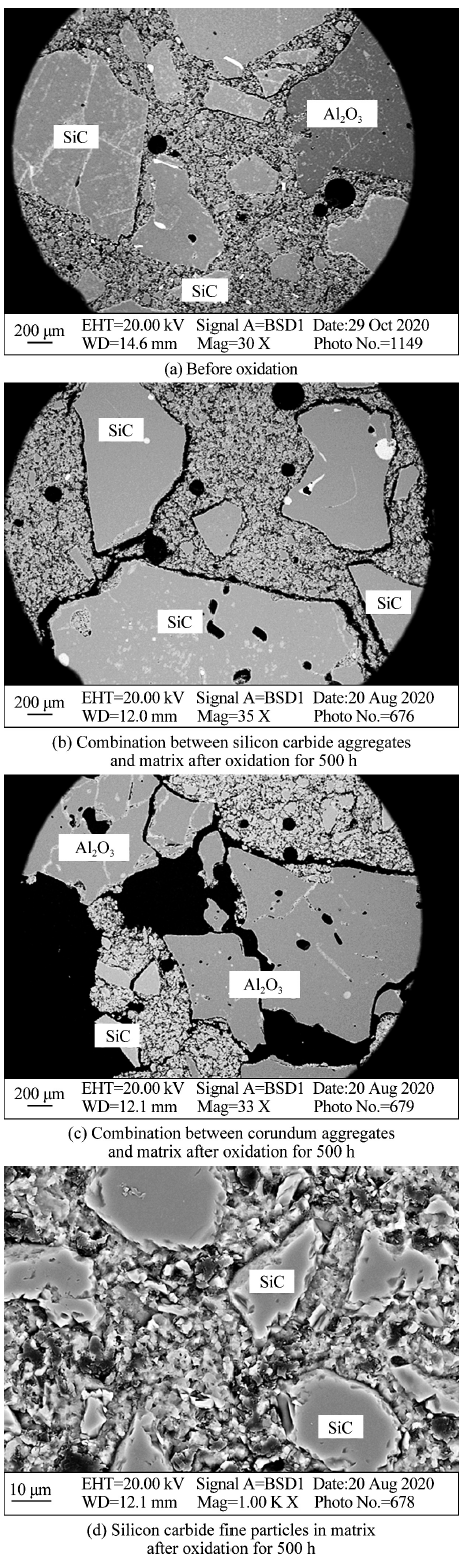
Steam Oxidation Resistance of Silicon Carbide Castables at Elevated Temperatures
SHI Huiying, WANG Jiaping*( ), WU Jiguang, HUANG Zhigang, QIN Hongbin
), WU Jiguang, HUANG Zhigang, QIN Hongbin
- Sinosteel Luoyang Institute of Refractories Research Co., Ltd., Luoyang 471039, China
-
Online:2021-09-15Published:2021-11-26 -
Contact:WANG Jiaping -
About author:Shi Huiying gained his bachelor’s degree from Wuhan University of Science and Technology in 2001 and his master’s degree from Tianjin University in 2008, respectively. Since 2001, he has been working in Sinosteel Luoyang Institute of Refractories Research Co., Ltd.
Cite this article
SHI Huiying, WANG Jiaping, WU Jiguang, HUANG Zhigang, QIN Hongbin. Steam Oxidation Resistance of Silicon Carbide Castables at Elevated Temperatures[J]. China's Refractories, 2021, 30(3): 23-27.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.cnref.cn/EN/10.19691/j.cnki.1004-4493.2021.03.005
| Starting materials | Sample 1# | Sample 2# |
|---|---|---|
| SiC particles | 56 | 41 |
| White fused corundum particles | 4 | 19 |
| SiC fines | 30 | 30 |
| Secar71 | 5 | 5 |
| Silica fume | 3 | 3 |
| Activated alumina powder | 2 | 2 |
| Additive (extra adding) | 0.12 | 0.12 |
Table 1 Formulations of specimens /mass%
| Starting materials | Sample 1# | Sample 2# |
|---|---|---|
| SiC particles | 56 | 41 |
| White fused corundum particles | 4 | 19 |
| SiC fines | 30 | 30 |
| Secar71 | 5 | 5 |
| Silica fume | 3 | 3 |
| Activated alumina powder | 2 | 2 |
| Additive (extra adding) | 0.12 | 0.12 |
| Item | Specimens 1# | Specimens 2# | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corundum | CA2 | Anorthite | Cristobalite | Total | Corundum | CA2 | Anorthite | Cristobalite | Total | |
| Before oxidation | 5 | 3 | 3 | <1 | 12 | 10-20 | 3 | 3 | <1 | 17-27 |
| Oxidation for 300 h | 5 | - | 10-20 | 5 | 20-30 | 10 | - | 10-20 | 5-10 | 25-40 |
| Oxidation for 500 h | 3 | - | 20 | 10 | 33 | 10 | - | 20-30 | 5-10 | 35-50 |
Table 2 Phase composition (excluded SiC) of samples before and after different oxidation durations /mass%
| Item | Specimens 1# | Specimens 2# | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corundum | CA2 | Anorthite | Cristobalite | Total | Corundum | CA2 | Anorthite | Cristobalite | Total | |
| Before oxidation | 5 | 3 | 3 | <1 | 12 | 10-20 | 3 | 3 | <1 | 17-27 |
| Oxidation for 300 h | 5 | - | 10-20 | 5 | 20-30 | 10 | - | 10-20 | 5-10 | 25-40 |
| Oxidation for 500 h | 3 | - | 20 | 10 | 33 | 10 | - | 20-30 | 5-10 | 35-50 |
| [1] | Lyu Huili. Application and rational choice of garbage incineration furnace. Industrial Furnace (in Chinese), 2013, 35(1):43-45, 58. |
| [2] | Hua Xia. Structure of garbage incinerator and its lining refractories. Industrial Heating (in Chinese), 2001 (3):28-33. |
| [3] | Thorsten Tonnesen, Rainer Telle. Quality control management of refractory SiC for waste incineration plants. Proceedings of UNITECR 2011, Kyoto, Japan: 1-E-4. |
| [4] | Li Hongxia. Refractories Handbook(in Chinese). Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2007: 93. |
| [5] | Jiang Dongliang, Li Longtu, Ouyang Shixi, Shi Jianlin. China Materials Engineering Canon: Inorganic Nonmetallic Materials Engineering (Volume 8) (in Chinese). Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2006: 180. |
| [6] | Jiang Shigui. Crystallography and Mineralogy(in Chinese). Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 1993: 246. |
| [7] | Wang Yuan. Relationship between thermal expansion coefficient and chemical composition of glass. Bulletin of The Chinese Ceramic Society (in Chinese), 1982(3):35-40. |
| [8] | Guo Haizhu, Yu Sen. Handbook on Refractory Raw Materials (in Chinese). Bejing: China Building Materials Industry Press, 2000: 126,449. |
| [1] | M. H. MOREIRA, H. PENG, S. Dal PONT, V. C. PANDOLFELLI. The Role of the Size Effect on the Drying of Refractory Castables—How Its Under-standing Could Narrow the Gap between Laboratory Studies and Industrial Reality [J]. China's Refractories, 2024, 33(2): 35-40. |
| [2] | WANG Li, LIU Shijie, WEI Haoyu, GUO Yanyan, GENG Shangrui, YAN Miaoxin, QIN Feng, GUO Yusen, Ma Juanjuan, DONG Binbin. Microwave-assisted Synthesis of Al4SiC4 and Its Effect on Properties of MgO-C Refractories [J]. China's Refractories, 2024, 33(1): 14-17. |
| [3] | LYU Chunjiang, CHANG Cheng, HUANG Yifei, CAO Huiyan, LI Jie, ZHU Chong. Preparation and Properties of SiC Assembled Large Block for Blast Furnace Tuyeres [J]. China's Refractories, 2023, 32(4): 1-7. |
| [4] | CAO Huiyan, FENG Yanbin, ZHANG Xinhua, HUANG Zhigang, LI Jie, WANG Xinhui, WU Jiguang. Development and Application of Multi-phase Nitrides Bonded Silicon Carbide Lintel Blocks for Dry Quenching Furnaces [J]. China's Refractories, 2023, 32(2): 7-11. |
| [5] | WANG Jiaping, WU Jiguang, HUANG Zhigang, LYU Chunjiang, WANG Wenwu. Steam Oxidation Resistance Comparison of Several Silicon Carbide Refractories at Elevated Temperatures [J]. China's Refractories, 2023, 32(2): 18-23. |
| [6] | CAO Zhuang, JIA Qingwei, ZHANG Jun, ZHOU Huijun, LI Jinfeng, HUN Xianlei, YAN Leixin, QIN Hongbin, ZHANG Sanhua. Effect of Different Silica Fumes on Properties of Al2O3-SiC-C Castables for Iron Trough [J]. China's Refractories, 2023, 32(2): 31-36. |
| [7] | GU Chenwei, WANG Zhanmin, ZHAO Shixian, SI Yaochen, XIA Miao. Formation of Polytypoids (12H and 21R) in High Temperature Nitrogen Atmosphere and Their Effects on SiC-MgAl2O4 Composites [J]. China's Refractories, 2023, 32(2): 45-50. |
| [8] | XU Guotao, ZHAO Yuan, WU Jie, ZHANG Honglei, LIU Li, ZHANG Yanwen, ZHOU Wangzhi. Discussion on Abnormal Corrosion and Material Selection of Hot Iron Ladles with Steel Scrap Addition [J]. China's Refractories, 2023, 32(1): 1-5. |
| [9] | TIAN Xuekun, ZHOU Chaojie, ZHANG Lei, ZHAO Fei, JIA Quanli, LIU Xinhong, ZHONG Xiangchong. Preparation of ZrB2-ZrO2-SiC Composite Powder by Carbothermal Reduction from Zircon [J]. China's Refractories, 2023, 32(1): 25-29. |
| [10] | LIU Zhenglong, DENG Chengji, YU Chao, DING Jun, ZHU Hongxi. Effect of C@SiC Composite Powder Addition on Properties of Al2O3-SiC-C Castables for Iron Trough [J]. China's Refractories, 2022, 31(4): 39-44. |
| [11] | Valeriy V. MARTYNENKO, Vladimir V. PRIMACHENKO, Pavlo O. KUSHCHENKO, Irina G. SHULIK, Ludmyla K. SAVINA. Effects of a Combined Silica-containing Additive on Structural and Rheological Properties of a Low-cement Silicon Carbide Castable [J]. China's Refractories, 2022, 31(2): 1-6. |
| [12] | LUO Huaming, CAI Binli, YUAN Zhenqiang, ZUO Genliang, Zhang Jingzheng, WANG Fengyu, LI Jinyu, WEI Yingfeng, SUN Huochang, ZHAN Huasheng. Application and Hydration Resistance of SiC Refractories for Water-cooled Wall of Waste Incinerators [J]. China's Refractories, 2022, 31(2): 12-16. |
| [13] | SUN Saiyang, MA Xiaoqing, WANG Xingwei, ZHAO Yong, ZHANG Ronghui, FEI Weibao. Erosion Mechanism of Al2O3-SiC Castables for Lining Maintenance in Blast Furnace Hearths [J]. China's Refractories, 2022, 31(2): 17-23. |
| [14] | CAO Huiyan, FENG Yanbin, ZHANG Haiyan, MA Zhaoyang, LI Jie, WANG Xinhui, WU Jiguang, YANG Wengang. Optimization and Simulation of Inclined Channel Area Lining for CDQ Ovens [J]. China's Refractories, 2022, 31(2): 24-29. |
| [15] | HAN Xiaoyuan, SHI Kai, XIA Yi, WANG Peixun, LIU Yang, SHANG Jianzhao. Effects of Three Silicon-based Raw Materials on Properties and Microstructure of MgO-Al-C Materials [J]. China's Refractories, 2021, 30(4): 30-35. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||