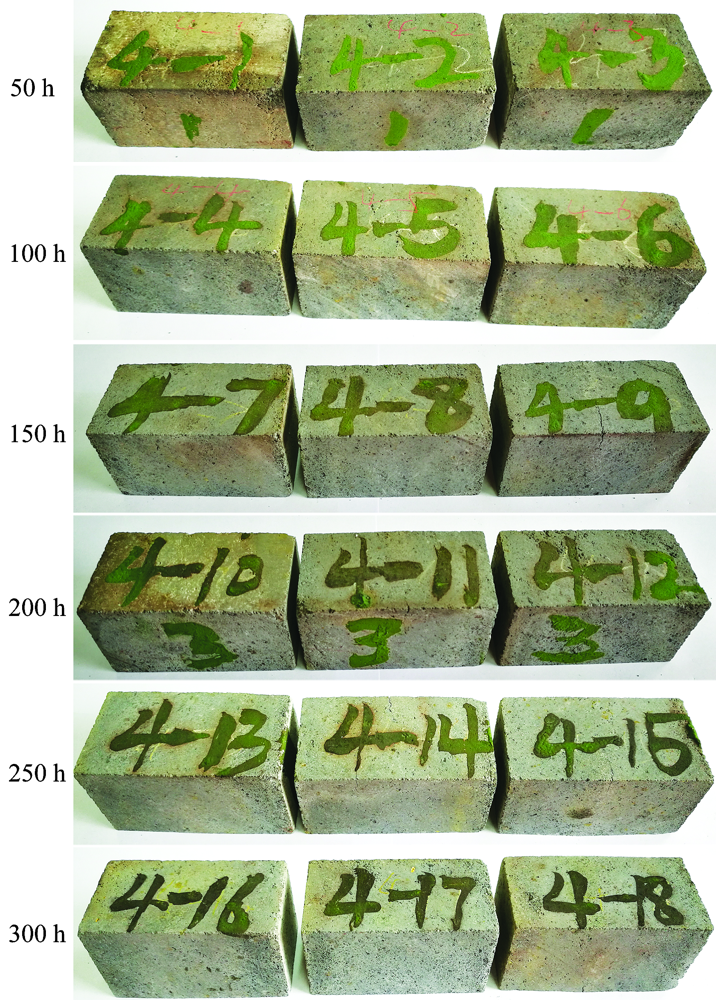
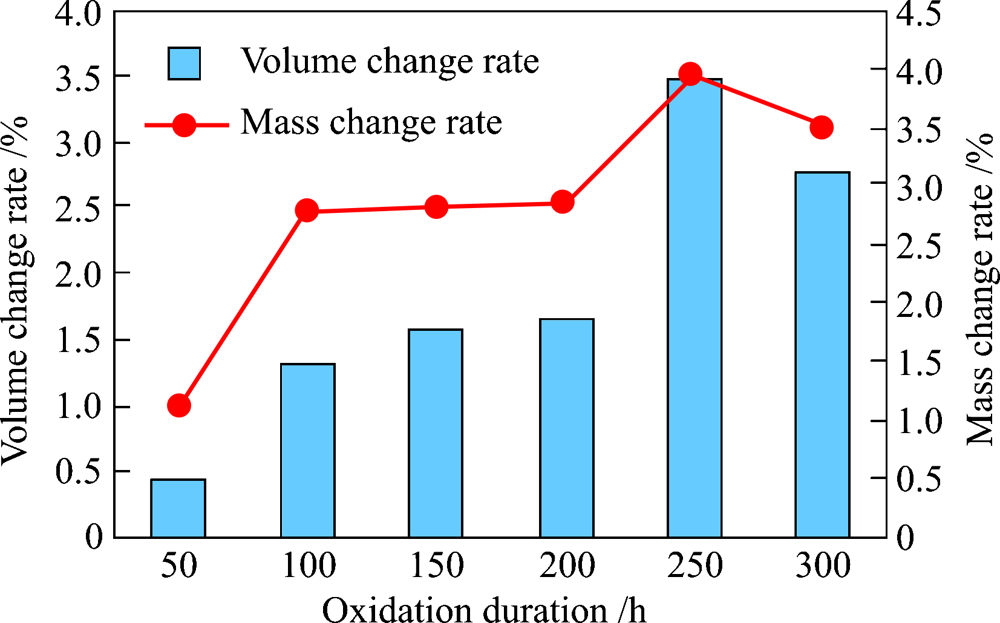
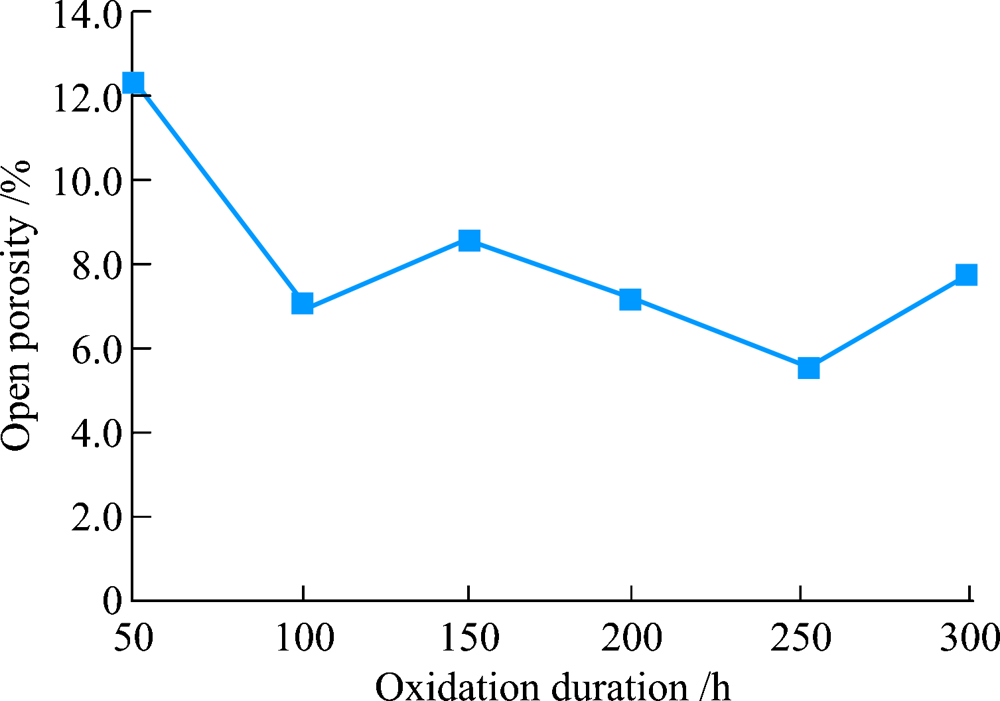
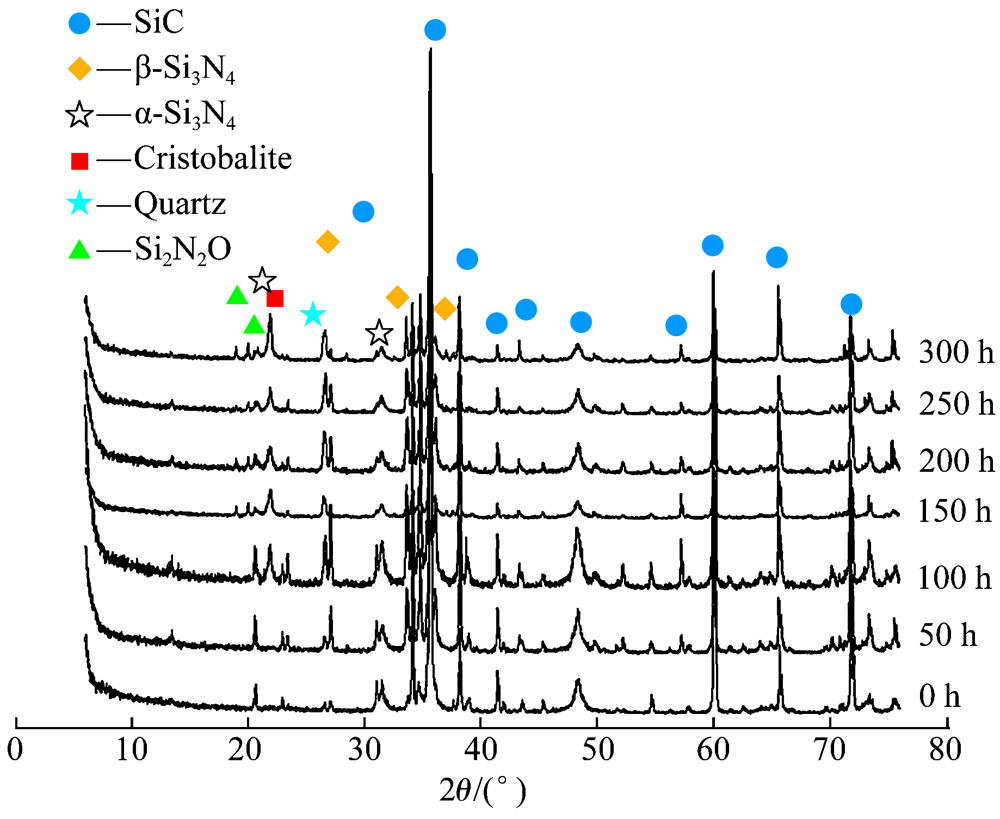
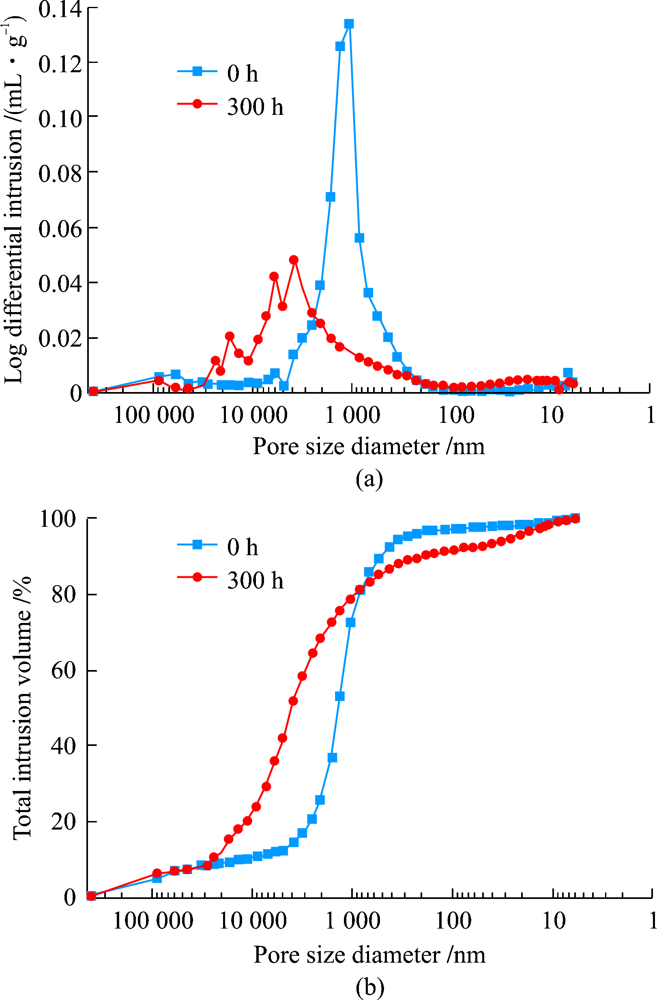
| [1] |
Valeriy V. MARTYNENKO, Iryna G. SHULYK, Yuliya Ye. MISHNYOVA, Tetyana G. TYSHYNA.
Investigation of Microstructure and Phase Composition of Chromic Oxide, AZS/Cr and High-alumina Refractories after Exposure of Basalt and Aluminaboronsilicate Glasses Melts
[J]. China's Refractories, 2024, 33(1): 1-6.
|
| [2] |
DU Juan, GUO Huishi, YANG Jialin, LI Wenfeng, GUI Yanghai, ZHAO Zhiqiang, LIU Yingfan.
Effects of Al2O3-SiO2 Raw Material Types on Properties of Anorthite Based Insulation Refractories
[J]. China's Refractories, 2024, 33(1): 23-27.
|
| [3] |
JIN Zhishang, SHAN Zhilin, ZHAO Huizhong, YU Jun, ZHANG Han.
Effect of Porogenic Agents on Properties of Microporous Mullite Aggregates
[J]. China's Refractories, 2023, 32(3): 31-35.
|
| [4] |
CAO Huiyan, ZHANG Xinhua, HUANG Yifei, WANG Wenwu, WU Jiguang, BU Xiangjuan, XU Haiyang.
Influence of Graphite on Molten-alkali Corrosion Resistance for β-SiAlON-SiC Materials
[J]. China's Refractories, 2022, 31(4): 22-27.
|
| [5] |
CHENG Shuiming, CHEN Jinfeng, WEI Jianxiu, CAI Wei, ZHAO Huizhong.
Effect of Submicron SiO2 Powder Addition on Properties of Cement Free Iron Trough Castables
[J]. China's Refractories, 2022, 31(3): 9-13.
|
| [6] |
YAN Mingwei, YANG Yumin, TONG Shanghao, ZHANG Jiayu, SUN Guangchao, LIU Kaiqi.
Phase Reconstruction and Microstructure Evolution of Magnesia-carbon Refractories at High Temperatures in Nitrogen
[J]. China's Refractories, 2022, 31(3): 14-23.
|
| [7] |
LYU Lihua, DING Donghai, XIAO Guoqing.
Combustion Synthesis of C/MgAl2O4 Composite Powders and Their Microstructure Evolution
[J]. China's Refractories, 2021, 30(4): 7-11.
|
| [8] |
LI Youqi, WANG Bingwei, ZHANG Yucui, BI Changlu, ZHAO Jizeng.
Effect of Industrial Alumina Powder Particle Size on Preparation of Active α-Al2O3 Micropowder
[J]. China's Refractories, 2021, 30(3): 11-16.
|
| [9] |
ZHANG Qi, YUAN Bo, WANG Gang, HAN Jianshen, ZHAO Xin.
Effect of Nitriding Process on Phase and Microstructure of Silicon Nitride Fibers Prepared by Direct Nitriding Method
[J]. China's Refractories, 2020, 29(4): 40-45.
|
| [10] |
GAO Zhenxin.
Phase Relationship at Subsolidus Tem-perature of MgO-MgAl2O4-ZrO2 Subsystem
[J]. China's Refractories, 2020, 29(1): 1-6.
|
| [11] |
HUANG Zhigang*, WANG Jiaping, LI Jie, CAO Huiyan, WU Jiguang.
Steam Oxidation Resistance of Nitride Bonded Silicon Carbide Refractories for Waste Incinerators at Elevated Temperatures
[J]. , 2019, 28(3): 4-7.
|
| [12] |
YI Shuai, DENG Lina, ZENG Luju, XUE Fei, PAN Chuancai, LIN Guowei, LIU Yueqiang, ZHANG Hang, XIE Jinli.
Effects of Chemical Composition and Microstructure on Exudation of Fused Cast AZS Refractory Materials
[J]. , 2019, 28(2): 23-26.
|
| [13] |
Debasish CHANDRA.
Comparison of Physico-mechanical Properties of TiO2 and Cr2O3 Additives on Reaction Sintered Zirconia-mullite Composites
[J]. , 2019, 28(1): 11-21.
|
| [14] |
YE Hang, SUN Gaoyang, ZHANG Haibo, LI Yanjing, GAO Changhe, LI Yong, YE Fangbao.
Investigation on Synthesis of Sintered Mullite from Low-medium Grade Kyanite
[J]. , 2019, 28(1): 22-30.
|
| [15] |
Andreas BÖRGER, Johan LORICOURT, Angelika PRIESE.
Influence of Impurities of Zircon Sand on the Microstructure of Fused Zirconia Grains for Continuous Casting of Steel Refractories
[J]. , 2018, 27(1): 1-7.
|
 ), HUANG Zhigang, ZHANG Xinhua, LIU Zhen
), HUANG Zhigang, ZHANG Xinhua, LIU Zhen