China's Refractories ›› 2020, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (1): 31-35.DOI: 10.19691/j.cnki.1004-4493.2020.01.006
• Original article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Influence of Setting Accelerating Agents on Properties of Colloidal Alumina Bonded Corundum Castables
ZHANG Xiaohui1,*(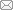 ), YU Xingguo1,3, WANG Baoyu2, ZHU Boquan3
), YU Xingguo1,3, WANG Baoyu2, ZHU Boquan3
- 1 Sinosteel Luoyang Institute of Refractories Research Co., Ltd., Luoyang 471039, China
2 Jiangsu Chianaref Refractory Co., Ltd., Yixing 214266, China
3 The State Key Laboratory of Refractories and Metallurgy, Wuhan University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430081, China
-
Online:2020-01-10Published:2020-01-10 -
Contact:ZHANG Xiaohui -
About author:Zhang Xiaohui was born in 1979. She obtained her bachelor’s degree with the major of inorganic nonmetallic materials in 2001 and master’s degree with the major of materials science in 2004 from Xi’an University of Architecture & Technology. From 2004 to the end of 2005, she worked in Xi’an Qinxiang Technology Co., Ltd. Since 2006, she has been working in Sinosteel Luoyang Institute of Refractories Research Co., Ltd.
Cite this article
ZHANG Xiaohui, YU Xingguo, WANG Baoyu, ZHU Boquan. Influence of Setting Accelerating Agents on Properties of Colloidal Alumina Bonded Corundum Castables[J]. China's Refractories, 2020, 29(1): 31-35.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.cnref.cn/EN/10.19691/j.cnki.1004-4493.2020.01.006
| Starting materials | A0# | A1# | A2# | A3# | A4# | A5# | A6# | A7# | C# |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tabular corundum (6-3 mm) | 23 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 23 |
| Tabular corundum (3-1 mm) | 23 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 23 |
| Tabular corundum (≤1 mm) | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 |
| Tabular corundum (≤0.044 mm) | 23 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 23 |
| CL370 micropowder | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 |
| Colloidal alumina (extra-adding) | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | |
| Water (extra-adding) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 |
| Urea (extra-adding) | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | ||
| Secar 71 (extra-adding) | 3 | ||||||||
| Magnesia fines (≤0.061 mm) (extra-adding) | 0.10 | 0.20 | 0.30 | ||||||
| Sodium meta-aluminate (extra-adding) | 0.05 | 0.10 | 0.30 |
Table 1 Formulations for specimens /mass%
| Starting materials | A0# | A1# | A2# | A3# | A4# | A5# | A6# | A7# | C# |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tabular corundum (6-3 mm) | 23 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 23 |
| Tabular corundum (3-1 mm) | 23 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 23 |
| Tabular corundum (≤1 mm) | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 |
| Tabular corundum (≤0.044 mm) | 23 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 23 |
| CL370 micropowder | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 |
| Colloidal alumina (extra-adding) | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | |
| Water (extra-adding) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 |
| Urea (extra-adding) | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | ||
| Secar 71 (extra-adding) | 3 | ||||||||
| Magnesia fines (≤0.061 mm) (extra-adding) | 0.10 | 0.20 | 0.30 | ||||||
| Sodium meta-aluminate (extra-adding) | 0.05 | 0.10 | 0.30 |
| Specimen No. | A0# | A1# | A2# | A3# | A4# | A5# | A6# | A7# | C# |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flow value /mm | 171 | 184 | 180 | 178 | 173 | 175 | 166 | 158 | 192 |
Table 2 Flow values of corundum castables with different formulations
| Specimen No. | A0# | A1# | A2# | A3# | A4# | A5# | A6# | A7# | C# |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flow value /mm | 171 | 184 | 180 | 178 | 173 | 175 | 166 | 158 | 192 |

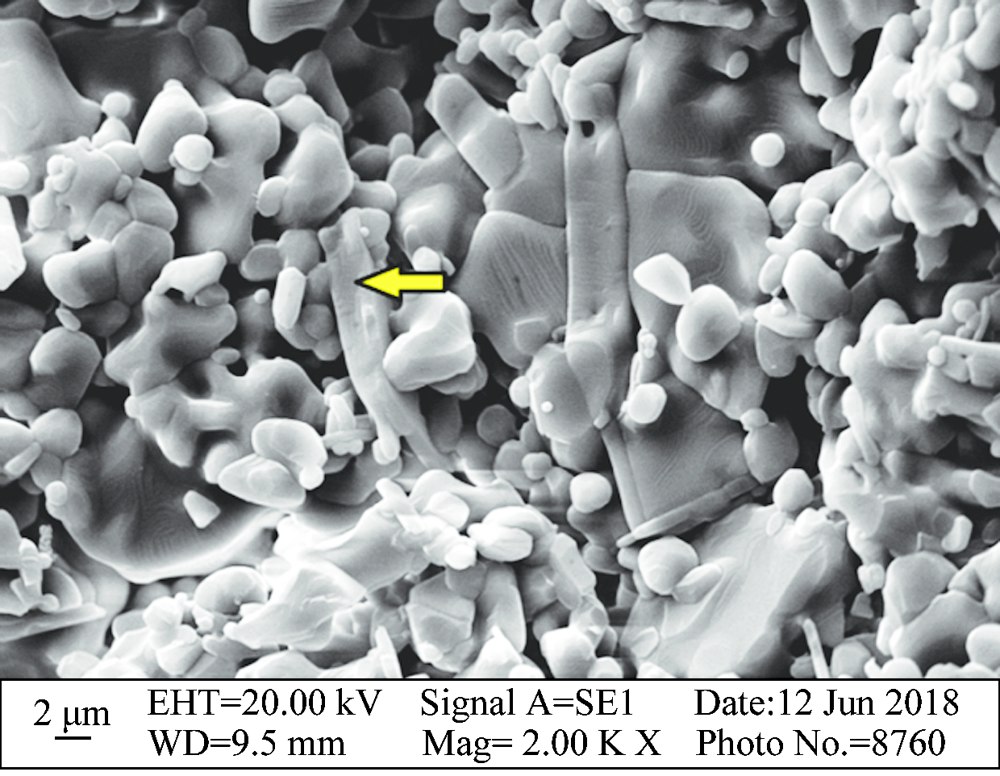
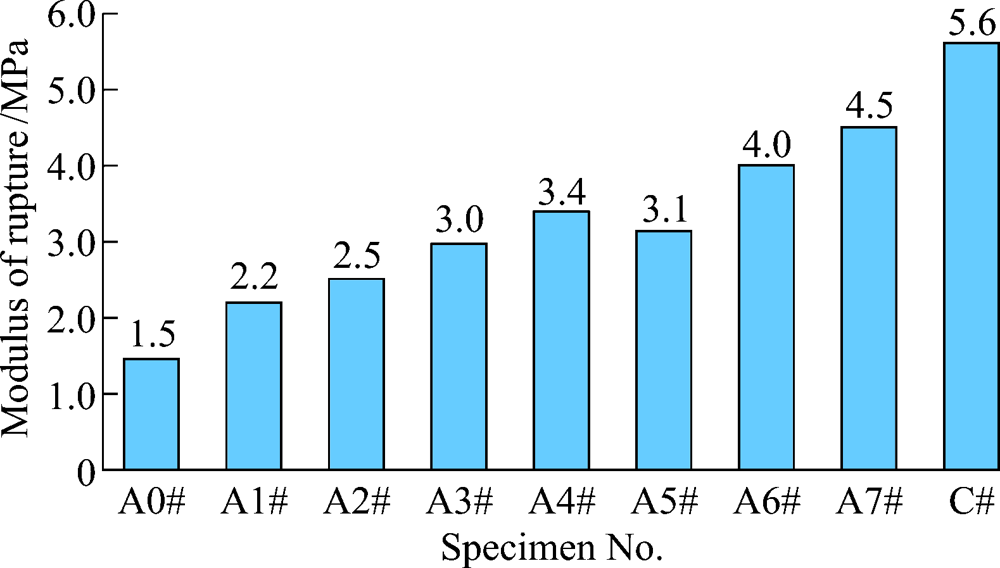
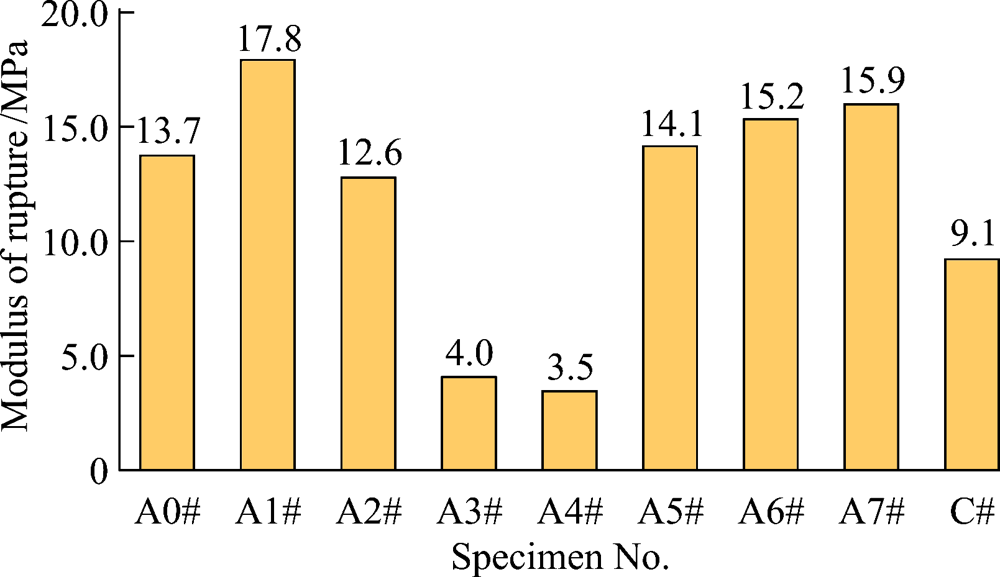
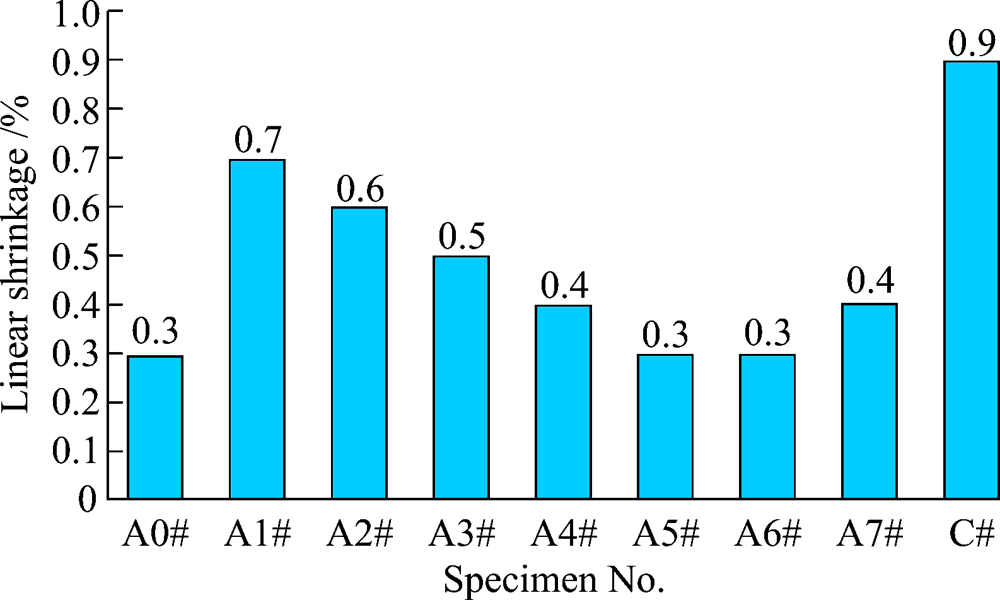
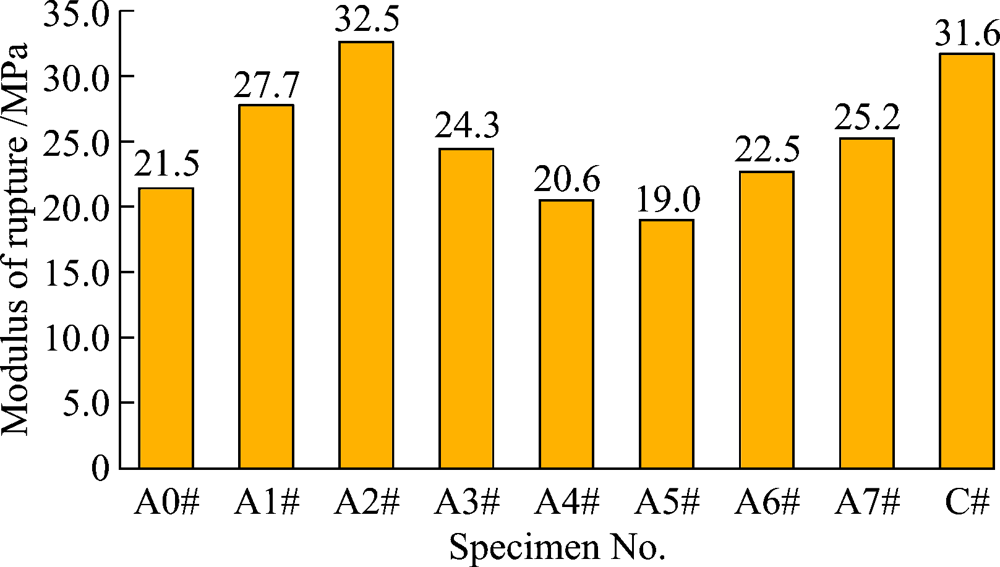
Fig. 3 Section morphology of colloidal alumina bonded corundum castable specimen after drying at 110 ℃ for 24 h (A3# with 0.5% urea and 0.2% magnesia fines)
| [1] | Zhang Xiaohui, Yu Xingguo, Wang Baoyu, Zhu Boquan . Influence of dispersants on flow ability of colloidal alumina bonded corundum castables. China’s Refractories, 2019,28(4):26-30. |
| [2] | Beate Balzer, Martin K, M. Hruschka, Ludwig J . Gauckler. In-situ rheological investigation of the coagulation in aqueous alumina suspensions. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2001,84(8):1733-1739. |
| [3] | Li Youqi, Li Yawei, Jin Shengli, Li Nan . Synthesis and its microstructure of calcium hexaluminate material by reaction sintering. Naihuo Cailiao (Refractories, in Chinese), 2004,38(5):318-323. |
| [1] | FAN Muxu, HOU Xiaojing, FENG Zhiyuan, WANG Han, LIU Pengcheng, SHI Gan. Alkali Vapor Corrosion of Different Refractories at High Temperatures [J]. China's Refractories, 2023, 32(2): 24-30. |
| [2] | GUO Peng, CHEN Lu, YU Tongshu, ZHANG Hui, WANG Dongdong. Effect of Zirconia Corundum Addition on Properties of Chrome Corundum Castables [J]. China's Refractories, 2023, 32(2): 41-44. |
| [3] | WANG Zhiqiang, LEI Zhongxing, XU Guotao, PENG Xiaoqian, ZHU Boquan, LIU Li, GUO Zongqi. Fabrication and Improving Properties of Lightweight Al2O3-MgO Castables for Ladle Working Lining [J]. China's Refractories, 2023, 32(1): 6-13. |
| [4] | WANG Huan, WANG Zhanmin, FENG Haixia, CAO Yingnan, LIU Jun, XU Yingshun. Effect of H2O2 Addition on Anti-explosion Performance of ρ-Al2O3 Bonded Corundum Castables [J]. China's Refractories, 2023, 32(1): 14-19. |
| [5] | WANG Jingran, CHEN Xinming, KE Changming, ZHANG Jinhua, LIU Xuexin, LI Wen. Rheological and Sintering Properties of Two Kinds of Corundum-spinel Micropowders [J]. China's Refractories, 2022, 31(4): 7-11. |
| [6] | GUO Xiaowei, XIN Guiyan, LEI Qizhen, XIONG Naling, SUN Feng, LI Shaoguang, SUN Gaoyang, LI Bing. Development of Dense Corundum-mullite Bricks for Blast Furnace Ceramic Pad [J]. China's Refractories, 2021, 30(4): 25-29. |
| [7] | GUO Liu, ZHAO Zongqiang, MA Junhua, CHEN Liugang. Effect of ZnO Precursor on Properties of Calcium Aluminate Cement Bonded Corundum Castables [J]. China's Refractories, 2021, 30(4): 36-39. |
| [8] | LI Ye, LIU Kun, DING Dafei, WANG Qingfeng, FU Xiaohui, YE Guotian. Effect of Curing Temperature on Intermediate Temperature Properties of Calcium Aluminate Cement Bonded Corundum Castables [J]. China's Refractories, 2021, 30(3): 33-36. |
| [9] | SU Chang, MA Beiyue, REN Xinming, LIU Guoqiang, ZHU Qiang. Effect of Starch Addition on Properties of Corundum-mullite Porous Ceramics [J]. China's Refractories, 2020, 29(4): 19-22. |
| [10] | GUO Hongxiang, SUN Xiaogai, JIA Quanli, LI Xueyan, LIU Xinhong. Effect of Calcium Chloride Addition on Properties of Corundum Spinel Castable [J]. China's Refractories, 2020, 29(4): 46-49. |
| [11] | Xiaowen WU, Peng CHI, Bohao CHENG, Yuena ZHANG, Wei SU, Xin MIN, Minghao FANG, Yan’gai LIU, Zhaohui HUANG. Research and Development of Recycling Utilization of Used Refractories: A Review [J]. China's Refractories, 2020, 29(3): 38-47. |
| [12] | XIA Wenbin, ZHAN Huasheng, LI Jinyu, LI Yanjing, MA Shulong, SU Yuzhu, ZHANG Jili, GAO Changhe. Effect of Andalusite Addition on Properties of Chrome-corundum Bricks [J]. China's Refractories, 2020, 29(2): 21-24. |
| [13] | YAN Huang, LUO Hui. Research and Application of Corundum Self-flowing Castables for Ladles [J]. , 2019, 28(2): 37-40. |
| [14] | LI Youqi, DING Jinxing, CUI Qingyang, ZHAO Jizeng. Application of Activated Alumina Powders in Corundum Castables [J]. , 2019, 28(2): 12-17. |
| [15] | ZHANG Ju, LONG Bin, ZHOU Yunpeng, Andreas BUHR, WANG Feng, CUI Qingyang, XIE Guofeng, DING Dafei, JIA Quanli, YE Guotian. Relation Between Sintering Reactivity of Matrix and Thermal Shock Resistance of Ultra-low Cement Bonded Corundum-spinel Castables for Fired Purging Plugs [J]. , 2018, 27(4): 13-20. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||