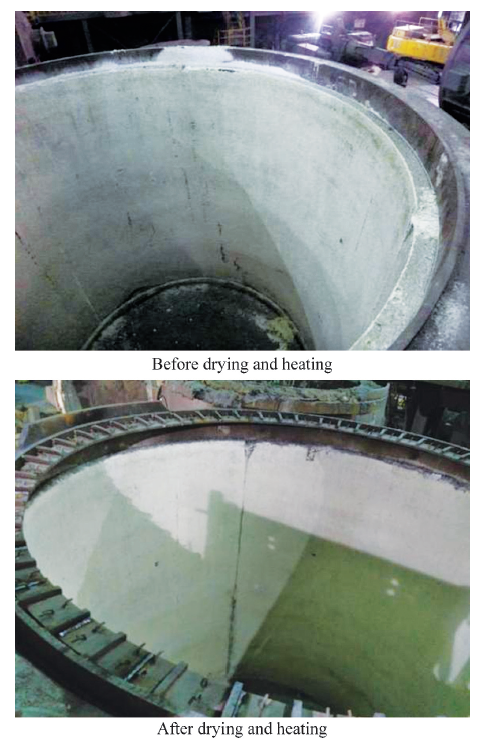
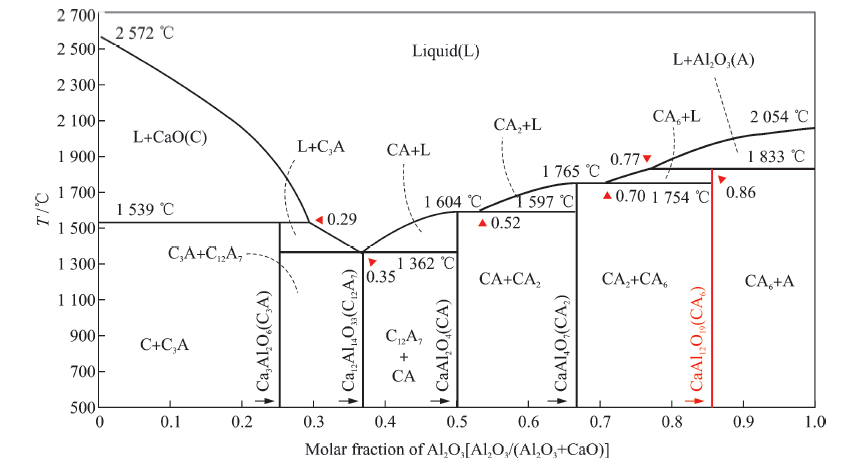
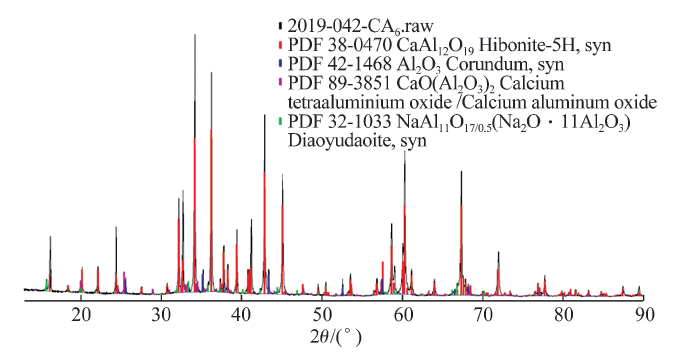
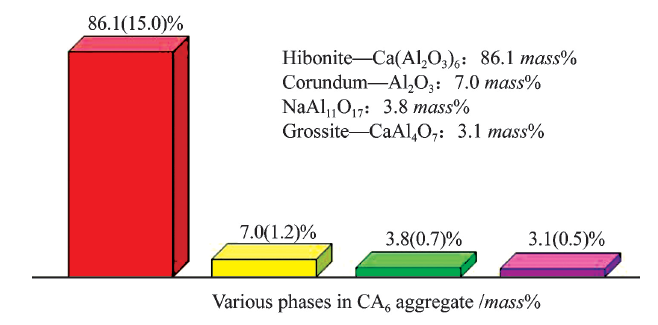
China's Refractories ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (1): 35-40.DOI: 10.19691/j.cnki.1004-4493.2021.01.006
• Original article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Insulating Permanent Lining of Calcium Hexaluminate Based Castable for 300t Ladle in Baosteel
GAN Feifang1,*( ), GUO Zongqi2, GAO Jianying3, GAO Hua1
), GUO Zongqi2, GAO Jianying3, GAO Hua1
- 1 Baoshan Iron & Steel Co., Ltd., Shanghai 201900, China
2 Trasteel International SA, Lugano CH-6900, Switzerland
-
Online:2021-03-15Published:2021-05-01 -
Contact:GAN Feifang -
About author:Gan Feifang has been engaged in research and development of refractory materials and applied technology for nearly 30 years, and has successively been in charge of and participated in more than 100 research projects of Baosteel. The main research directions are as follows: new technology development of energy-saving and environmental protection refractory materials for high-temperature metallurgical furnaces, development of refractories for smelting various steels, refractories for refining furnace and ladle, refractory materials for hot metal pretreatment and blast furnace taphole, clay development. The research results promote the technological progress of iron and steel metallurgy refractory materials.
Cite this article
GAN Feifang, GUO Zongqi, GAO Jianying, GAO Hua. Insulating Permanent Lining of Calcium Hexaluminate Based Castable for 300t Ladle in Baosteel[J]. China's Refractories, 2021, 30(1): 35-40.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.cnref.cn/EN/10.19691/j.cnki.1004-4493.2021.01.006
| CA6 raw material | Chemical composition /mass% | Physical properties | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | CaO | R2O | AP/% | WA/% | BD/ (g · cm-3) | |
| CA6N1 | 0.50 | 90.00 | 0.08 | 7.70 | 0.09 | 26.8 | 9.9 | 2.70 |
| CA6N2 | 0.11 | 91.90 | 0.04 | 7.50 | 0.04 | 25.5 | 9.2 | 2.78 |
Table 1 Chemical and physical properties of calcium hexaluminate aggregates
| CA6 raw material | Chemical composition /mass% | Physical properties | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | CaO | R2O | AP/% | WA/% | BD/ (g · cm-3) | |
| CA6N1 | 0.50 | 90.00 | 0.08 | 7.70 | 0.09 | 26.8 | 9.9 | 2.70 |
| CA6N2 | 0.11 | 91.90 | 0.04 | 7.50 | 0.04 | 25.5 | 9.2 | 2.78 |
| Additional raw material | Chemical composition /mass% | Particle size/µm | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | CaO | TiO2 | ||
| Tabular alumina | 0.08 | 99.44 | 0.04 | 0.14 | 0.02 | < 45 |
| Calcined alumina | 0.01 | 99.84 | 0.02 | 0.07 | 0.02 | < 5 |
| Calcium aluminate cement | 0.20 | 69.19 | 0.06 | 29.92 | MgO: 0.22 | < 20 |
Table 2 Chemical and physical properties of additional raw materials
| Additional raw material | Chemical composition /mass% | Particle size/µm | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | CaO | TiO2 | ||
| Tabular alumina | 0.08 | 99.44 | 0.04 | 0.14 | 0.02 | < 45 |
| Calcined alumina | 0.01 | 99.84 | 0.02 | 0.07 | 0.02 | < 5 |
| Calcium aluminate cement | 0.20 | 69.19 | 0.06 | 29.92 | MgO: 0.22 | < 20 |
| Castable | Chemical composition /mass% | Bulk density/ (g · cm-3) | Apparent porosity/% | CCS/ MPa | CMOR/ MPa | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | Al2O3 | MgO | Fe2O3 | CaO | |||||
| CA6N1 | 0.18 | 89.59 | 0.21 | 0.11 | 8.41 | 2.62 | 25 | 51.1 | 16 |
| CA6N2 | - | - | - | - | - | 2.63 | 23 | 47.9 | 14.7 |
| High alumina | 19.28 | 69.88 | 3.92 | 1.43 | 2.30 | 2.85 | 11 | 105.5 | 10 |
Table 3 Chemical and physical properties of permanent lining materials
| Castable | Chemical composition /mass% | Bulk density/ (g · cm-3) | Apparent porosity/% | CCS/ MPa | CMOR/ MPa | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | Al2O3 | MgO | Fe2O3 | CaO | |||||
| CA6N1 | 0.18 | 89.59 | 0.21 | 0.11 | 8.41 | 2.62 | 25 | 51.1 | 16 |
| CA6N2 | - | - | - | - | - | 2.63 | 23 | 47.9 | 14.7 |
| High alumina | 19.28 | 69.88 | 3.92 | 1.43 | 2.30 | 2.85 | 11 | 105.5 | 10 |
| Physical properties and their testing conditions | CA6N1 castable | CA6N2 castable | High alumina castable | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Apparent porosity/% | 1 500 °C × 3 h | 32 | 31 | 13 |
| Bulk density/(g · cm-3) | 1 500 °C × 3 h | 2.55 | 2.56 | 2.76 |
| Modulus of rupture/MPa | 1 500 °C × 3 h | 31.6 | 30.8 | 12.6 |
| Cold crushing strength/MPa | 1 500 °C × 3 h | 161.8 | 177.5 | 95.5 |
| Permanent linear change/% | 1 500 °C × 3 h | 0 | +0.01 | +1.3 |
| Hot modulus of rupture/MPa | 1 400 °C × 1 h | 16.2 | 17.8 | < 3 |
| Thermal shock resistance/cycle | 1 100 °C-water cooling | 30 | 30 | 30 |
| Thermal conductivity/(W · m-1 · K-1) | 500 °C in average | 0.50 | 0.51 | 0.69 |
Table 4 Physical properties of castable after heating at high temperatures
| Physical properties and their testing conditions | CA6N1 castable | CA6N2 castable | High alumina castable | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Apparent porosity/% | 1 500 °C × 3 h | 32 | 31 | 13 |
| Bulk density/(g · cm-3) | 1 500 °C × 3 h | 2.55 | 2.56 | 2.76 |
| Modulus of rupture/MPa | 1 500 °C × 3 h | 31.6 | 30.8 | 12.6 |
| Cold crushing strength/MPa | 1 500 °C × 3 h | 161.8 | 177.5 | 95.5 |
| Permanent linear change/% | 1 500 °C × 3 h | 0 | +0.01 | +1.3 |
| Hot modulus of rupture/MPa | 1 400 °C × 1 h | 16.2 | 17.8 | < 3 |
| Thermal shock resistance/cycle | 1 100 °C-water cooling | 30 | 30 | 30 |
| Thermal conductivity/(W · m-1 · K-1) | 500 °C in average | 0.50 | 0.51 | 0.69 |
| [1] | Yufeng Wang, Sunday Araham, Rick Bodnar, Gary Brown, Brian Ruffner. An optimized ladle refractory configuration for steel refining and vacuum degassing processes at SSAB Americas. Proceedings of AISTech 2017, Tennessee, USA, 2017: 1587-1596. |
| [2] | Andreas Buhr. Refractories for steel secondary metallurgy. CN-Refractories, 1999,6(3):19-30. |
| [3] | J. Sakihama, R. Salomão. Microstructure development in porous calcium hexaluminate and application as a high-temperature thermal insulator: a critical review. Interceram: International Ceramic Review, 2019,68(6):66-71. |
| [4] | E. Criado, S. de Aza. Calcium hexaluminate as refractory materials. Proceedings of UNITECR 1991, Aachen, Germany, 1991: 403-407. |
| [5] | Cristina Domlnguez, Jerome Chevalier, Ramon Torrecillas, Gibert Fantozzi. Microstructure development in calcium hexaluminate. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2001,21(3):381-387. |
| [6] | Junhong Chen, Haiyang Chen, Mingwei Yan, Zheng Cao, Wenjun Mi. Formation mechanism of calcium hexaluminate. International Journal of Minerals, Metallurgy and Materials, 2016,23(10):1225-1230. |
| [7] | D. Asmi, I. M. Low. Self-reinforced Ca-hexaluminate alumina composites with graded microstructures. Ceramics International, 2008,34(2):311-316. |
| [8] | Gunter Büchel, Andreas Buhr, Dagmar Gierisch. Bonite—a new raw material alternative for refractory innovations. Proceedings of UNITECR2005, Florida, USA, 2005: 462-467. |
| [9] | M. Schnabel, A. Buhr, G. Büchel, R. Kockegey-Lorenz, J. Dutton. Advantages of calcium hexaluminate in a corrosive environment. Refractories Worldforum, 2011,3(4):87-94. |
| [10] | Dagmar Schmidtmeier, Rainer Kockegey-Lorenz, Andreas Buhr, Marion Schnabel, Jerry Dutton. Material design for new insulating lining concepts. Proceedings of 55th International Colloquium on Refractories, Aachen, Germany, 2012: 156-159. |
| [11] | D. Van Garsel, V. Gnauk, G. W. Kriechbaum, I. Stinneβen. New insulation raw material for high temperature applications. Proceedings of 41st International Colloquium on Refractories, Aachen, Germany, 1998: 122-128. |
| [12] | Hartmut Wuthnow, Jürgen Pötschke, Andreas Buhr, Frank Pözun. Experience with microporous calcium hexaluminate insulating materials in steel reheating furnace at Hoesch Hohenlimburg and Thyseen Krupp Stahl AG Bochum. Proceedings of 47th International Colloquium on Refractories, Aachen, Germany, 2004: 198-204. |
| [13] | Rainer Kockegey-Lorenz, Andreas Buhr, Raymond P. Racher. Industrial application experiences with microporous calcium hexaluminate insulating material SLA-92. Proceedings of 48th International Colloquium on Refractories, Aachen, Germany, 2005: 66-70. |
| [14] | Andreas Overhoff, Andreas Buhr, Jürgen Grass, Hartmut Wuthnow. New microporous materials for use in modern firing plants. CFI/Ber. DKG, 2005,82(8):E2-E5. |
| [15] | Marion Schnabel, Andreas Buhr, Doris Van Garsel, Dagmar Schmidtmeier. Advantages of dense calcium hexaluminate aggregate for back lining in steel ladles. Proceedings of UNITECR2009, Salvador, Brazil, 2009: 049. |
| [16] | Guo Zongqi, Zamboni Stefano, Gan Feifang, Gao Jianying. Multifunctional refractory-lined vessel: ladle aggregate. China’s Refractories, 2021,30(1):1-6. |
| [1] | Carlos PAGLIOSA, Leandro ROCHA, Marcelo BORGES, Celio CAVALCANTE. Novel Brick Technology for Carbon Reduction Footprint in Steel Shop Linings [J]. China's Refractories, 2024, 33(2): 16-21. |
| [2] | M. H. MOREIRA, H. PENG, S. Dal PONT, V. C. PANDOLFELLI. The Role of the Size Effect on the Drying of Refractory Castables—How Its Under-standing Could Narrow the Gap between Laboratory Studies and Industrial Reality [J]. China's Refractories, 2024, 33(2): 35-40. |
| [3] | LEE Yaotsung, ZHAO Lite, LEE Johnson, LIU William. Analysis of Corrosion Mechanisms of Low-cement or No-cement Al2O3-MgO Gunning Mix with Special Calcined Alumina in Rotary Slag Test [J]. China's Refractories, 2023, 32(4): 16-21. |
| [4] | ZAN Wenyu, MA Beiyue. Preparation of Lightweight Alumina-silica Castables by Replacing Closed-cell Perlite Aggregates with Coal Gangue Ceramsites [J]. China's Refractories, 2023, 32(3): 20-25. |
| [5] | ZHANG Hongrui, CHEN Liugang. Binder Effect on Properties of Cr2O3-bearing Corundum-based Refractory Castables [J]. China's Refractories, 2023, 32(3): 36-41. |
| [6] | CAO Zhuang, JIA Qingwei, ZHANG Jun, ZHOU Huijun, LI Jinfeng, HUN Xianlei, YAN Leixin, QIN Hongbin, ZHANG Sanhua. Effect of Different Silica Fumes on Properties of Al2O3-SiC-C Castables for Iron Trough [J]. China's Refractories, 2023, 32(2): 31-36. |
| [7] | XU Guotao, ZHAO Yuan, WU Jie, ZHANG Honglei, LIU Li, ZHANG Yanwen, ZHOU Wangzhi. Discussion on Abnormal Corrosion and Material Selection of Hot Iron Ladles with Steel Scrap Addition [J]. China's Refractories, 2023, 32(1): 1-5. |
| [8] | WANG Zhiqiang, LEI Zhongxing, XU Guotao, PENG Xiaoqian, ZHU Boquan, LIU Li, GUO Zongqi. Fabrication and Improving Properties of Lightweight Al2O3-MgO Castables for Ladle Working Lining [J]. China's Refractories, 2023, 32(1): 6-13. |
| [9] | WANG Huan, WANG Zhanmin, FENG Haixia, CAO Yingnan, LIU Jun, XU Yingshun. Effect of H2O2 Addition on Anti-explosion Performance of ρ-Al2O3 Bonded Corundum Castables [J]. China's Refractories, 2023, 32(1): 14-19. |
| [10] | SHEN Mingke, LUO Ming, HU Chengyang, YU Yan, SONG Yanan, NI Feijiang, LI Jin. Effects of Four Kinds of Alumina Micropowder on Properties of Al2O3-C Refractories [J]. China's Refractories, 2022, 31(4): 34-38. |
| [11] | LIU Zhenglong, DENG Chengji, YU Chao, DING Jun, ZHU Hongxi. Effect of C@SiC Composite Powder Addition on Properties of Al2O3-SiC-C Castables for Iron Trough [J]. China's Refractories, 2022, 31(4): 39-44. |
| [12] | SUN Saiyang, MA Xiaoqing, WANG Xingwei, ZHAO Yong, ZHANG Ronghui, FEI Weibao. Erosion Mechanism of Al2O3-SiC Castables for Lining Maintenance in Blast Furnace Hearths [J]. China's Refractories, 2022, 31(2): 17-23. |
| [13] | LUO Ming, FANG Binxiang, WEI Guoping, LIU Guangping, SHEN Mingke, SONG Yanan. Development and Application of Carbon-free Al2O3-MgO Dense Bricks for Steel Ladles [J]. China's Refractories, 2022, 31(2): 35-39. |
| [14] | SONG Yanan, WEI Guoping, CHEN Qin, SHUAI Hang, LIU Guangping, SHEN Mingke, CHEN Yaosheng, YU Yan, WANG Yulong, CAO Yaping. Effect of Various Alumina Powders on Properties of Castables [J]. China's Refractories, 2022, 31(2): 45-48. |
| [15] | GUO Liu, ZHAO Zongqiang, MA Junhua, CHEN Liugang. Effect of ZnO Precursor on Properties of Calcium Aluminate Cement Bonded Corundum Castables [J]. China's Refractories, 2021, 30(4): 36-39. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||