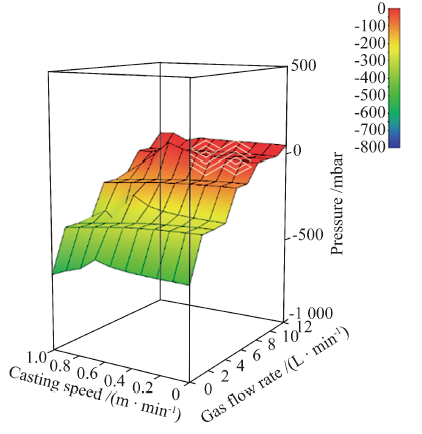
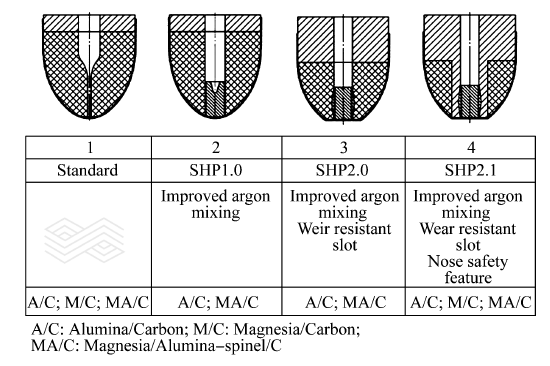
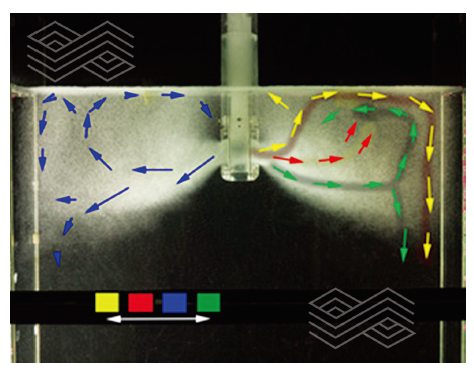
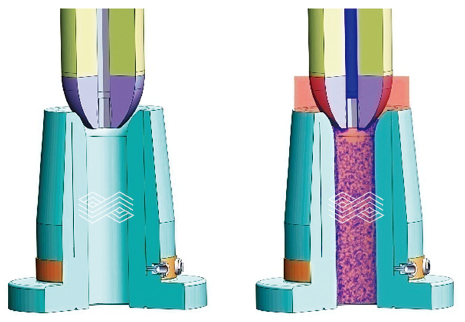
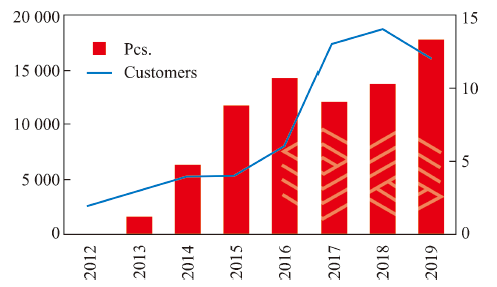
| [1] |
E. B. Pretorius, H. G. Oltmann, B. T. Schart. An overview of steel cleanliness from an industry perspective. AISTech 2013 conference Proceedings, 993-1026.
|
| [2] |
J M Galpin, P Naveau, H Visser, G. Sussek. An investigation on the mechanism of gas bubbles/inclusions entrapment in the solidified steel shell. Publications Office of the EU, 2005.
|
| [3] |
Ville Liisanantti, Jarno Pirinen, Jarkko Makala, Hannu Nevala. Benefits of stopper rods argon injection at Ruuki production Raahe works. ECCC2008.
|
| [4] |
Pavel Ernesto Ramirez Lopez, Pooria Nazem Jalali, Christer Nilsson. Adding argon injection to an advanced model for continuous casting of steel. 8th European Continuous Casting Conference, Graz, Austria, 2014.
|
| [5] |
Brian G., Thomas, Alex Dennisov, Hua Bai. Behavior of argon bubbles during continuous casting of steel. ISS 80th Steelmaking Conference, Proceedings, Chicago, USA, 1997 (80):375-384.
|
| [6] |
Gernot Hackl, Yong Tang, Gerald Nitzl, Chalmers D, Dorricott J.D., Heaslip L.J. Flow control refractory design optimization of submerged-entry nozzles by simulation technology. Proc. AISTech 2013 Proceedings.
|
| [7] |
Yong Tang, Gerald Nitzl, Gernot Hackl. Novel stopper designs to improve argon purging efficiency in slab casting. Proceedings of ISR2016, 2016, Zhengzhou, China.
|
| [8] |
KrumpelG., RHIAG, Austria, FuchsR., voestalpine Stahl LinzGmbH, Austria, PoschW., voestalpine Stahl LinzGmbH., Austria, MichelitschA., RHIAG., Austria, HacklG., RHIAG., Austria. Optimized Argon supply from tundish to mould by using the SHP stopper. METEC & 2nd ESTAD 2015, Düsseldorf, Germany.
|
 ), Xiaohui LIU2, Qingxin LIU2, Jie SHEN3, Yong TANG4
), Xiaohui LIU2, Qingxin LIU2, Jie SHEN3, Yong TANG4