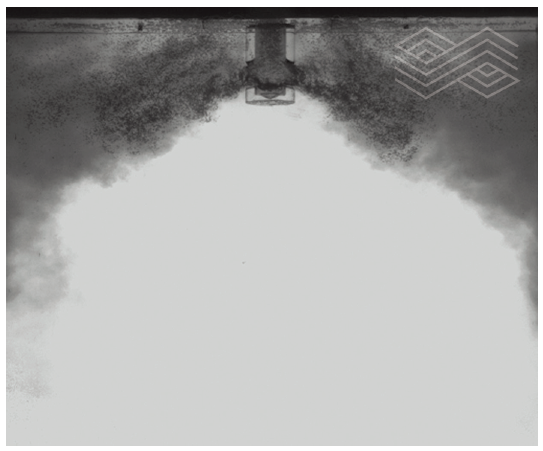
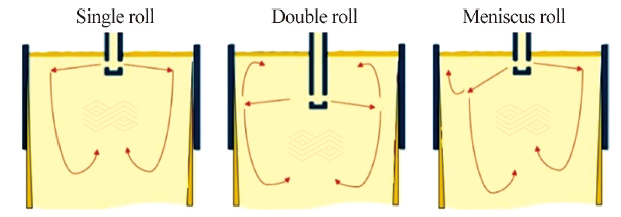
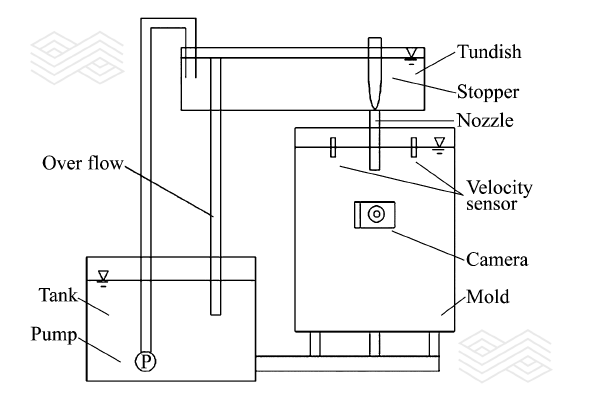
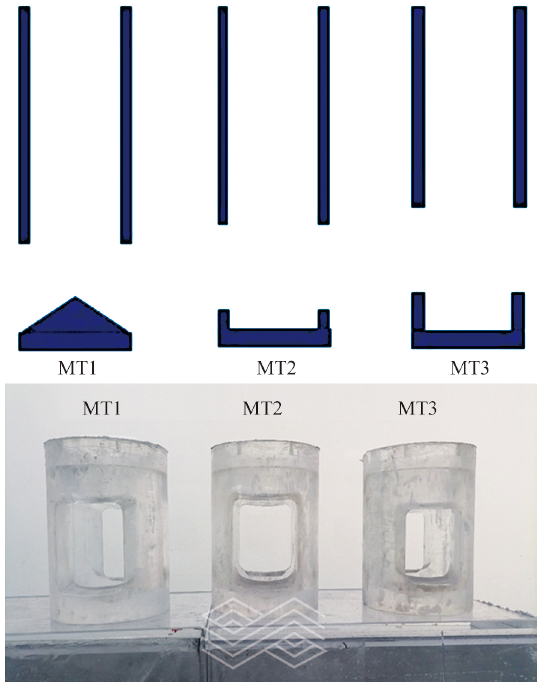
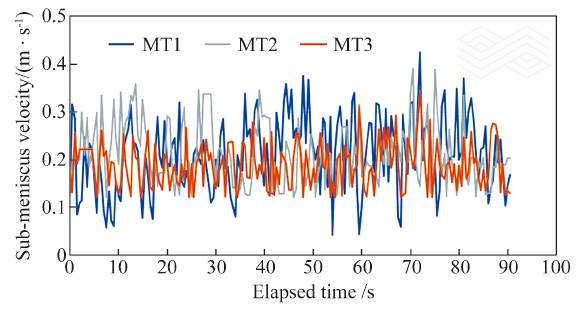
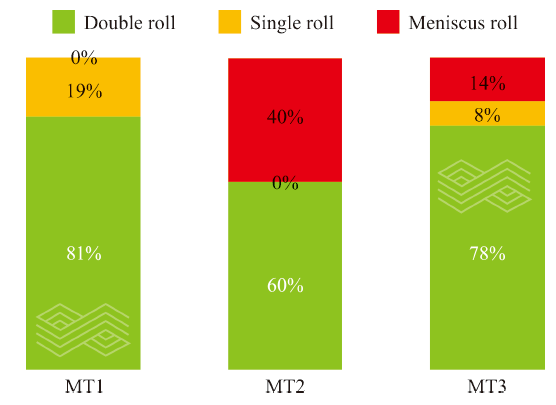
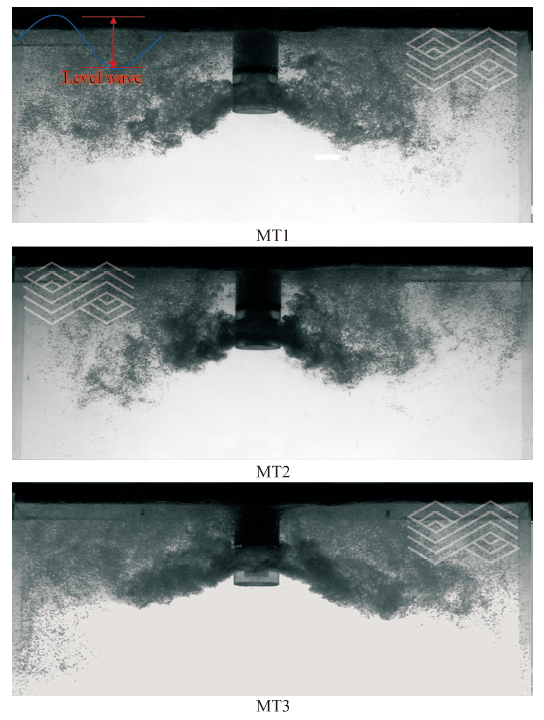
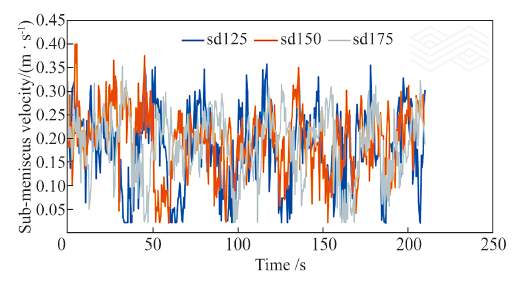
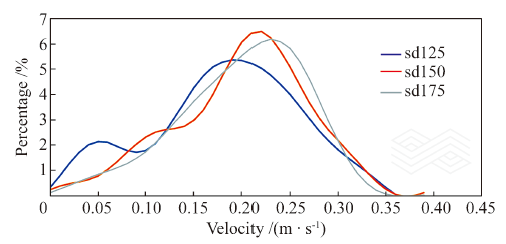
| [1] |
Somnath Basu, Shiv Kumar Choudhary, Narendra U. Girase. Nozzle clogging behaviour of Ti-bearing Al-killed ultra low carbon steel. ISIJ International, 2004, 44(10):1653-1660.
DOI
URL
|
| [2] |
Deng X., Ji C., Cui Y., Li L., Yin X., Yang Y., Mclean A. Flow pattern control in continuous slab casting moulds: physical modelling and plant trials. Ironmaking & Steelmaking, 2017, 44(6):461-471.
|
| [3] |
Qing Fang, Hongwei Ni, Hua Zhang, Bao Wang, Zean Lv. The effects of a submerged entry nozzle on flow and initial solidification in a continuous casting bloom mold with electromagnetic stirring. Metals-Open Access Metallurgy Journal, 2017, 7(4):146.
|
| [4] |
Somnath Kumar, Keshari K.K., Gupta Antariksh, Prasad Abdhesh, Kumar Vikash, Mishra Basudev, Abhishek Kumar. Improvement in castability of Al-killed steel in billet casters by process optimization. Transactions of the Indian Institute of Metals, 2020, 73(1):243-249.
DOI
|
| [5] |
Franc Tehovnik, Jaka Burja, Boštjan Arh, Matjaz Knap. Submerged entry nozzle clogging during continuous casting of Al-killed steel. Metalurgija, 2015, 54(2):371-374.
|
| [6] |
Vermeulen Y, Coletti B, Blanpain B, Wollants P, Vleugels J. Material evaluation to prevent nozzle clogging during continuous casting of Al killed steels. ISIJ International, 2002, 42(11):1234-1240.
DOI
URL
|
| [7] |
Lifeng Zhang, Subo Yang, kaike Cai, Jiying Li, Xiaoguang Wan, Brian G. Thomas. Investigation of fluid flow and steel cleanliness in the continuous casting strand. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2007, 38B(1):63-83.
|
| [8] |
Tao Zhang, Jian Yang, Peng Jiang. Measurement of molten steel velocity near the surface and modeling for transient fluid flow in the continuous casting mold. Metals, 2019, 9(1):36.
DOI
URL
|
| [9] |
J.-F. Domgin, Pascal Gardin, Jean-Marie Galpin, A. Dez. Effect of process parameters variation on CC mould-hydrodynamics and inclusions behavior. Revue de Métallurgie, 2005, 102(10)
|
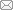 ), Tianfei MA1, Gernot HACKL2, Jianhua LUO3, Gongjie TAO3
), Tianfei MA1, Gernot HACKL2, Jianhua LUO3, Gongjie TAO3