China's Refractories ›› 2020, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (4): 6-9.DOI: 10.19691/j.cnki.1004-4493.2020.04.002
• Original article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of Pore Size on Properties of Highly Porous Silica Ceramic Foams for Heat Insulation
DU Zhongpei1,2, YAO Dongxu1, XIA Yongfeng1,*( ), ZUO Kaihui1, YIN Jinwei1, LIANG Hanqin1, ZENG Yuping1,*(
), ZUO Kaihui1, YIN Jinwei1, LIANG Hanqin1, ZENG Yuping1,*( )
)
- 1 State Key Laboratory of High Performance Ceramics and Superfine Microstructure, Shanghai Institute of Ceramics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 200050, China
2 Center of Materials Science and Optoelectronics Engineering, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
-
Online:2020-12-15Published:2020-12-15 -
Contact:XIA Yongfeng,ZENG Yuping -
About author:Du Zhongpei is pursuing his PhD in Shanghai Institute of Ceramics, Chinese Academy of Sciences. His project is the manufacturing of highly porous ceramic foams with tailored pore structures, and he has already published 6 papers in Journals.
Cite this article
DU Zhongpei, YAO Dongxu, XIA Yongfeng, ZUO Kaihui, YIN Jinwei, LIANG Hanqin, ZENG Yuping. Effect of Pore Size on Properties of Highly Porous Silica Ceramic Foams for Heat Insulation[J]. China's Refractories, 2020, 29(4): 6-9.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.cnref.cn/EN/10.19691/j.cnki.1004-4493.2020.04.002
| Samples | S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Commercial fused silica powder | 48.2 | 48.2 | 48.2 | 48.2 |
| α-Si3N4 powder | 9.9 | 9.9 | 9.9 | 9.9 |
| IBMA | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Mixed surfactants | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 |
| Deionized water | 41.3 | 41.2 | 41.1 | 41.0 |
Table 1 Sample formulations /mass%
| Samples | S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Commercial fused silica powder | 48.2 | 48.2 | 48.2 | 48.2 |
| α-Si3N4 powder | 9.9 | 9.9 | 9.9 | 9.9 |
| IBMA | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Mixed surfactants | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 |
| Deionized water | 41.3 | 41.2 | 41.1 | 41.0 |
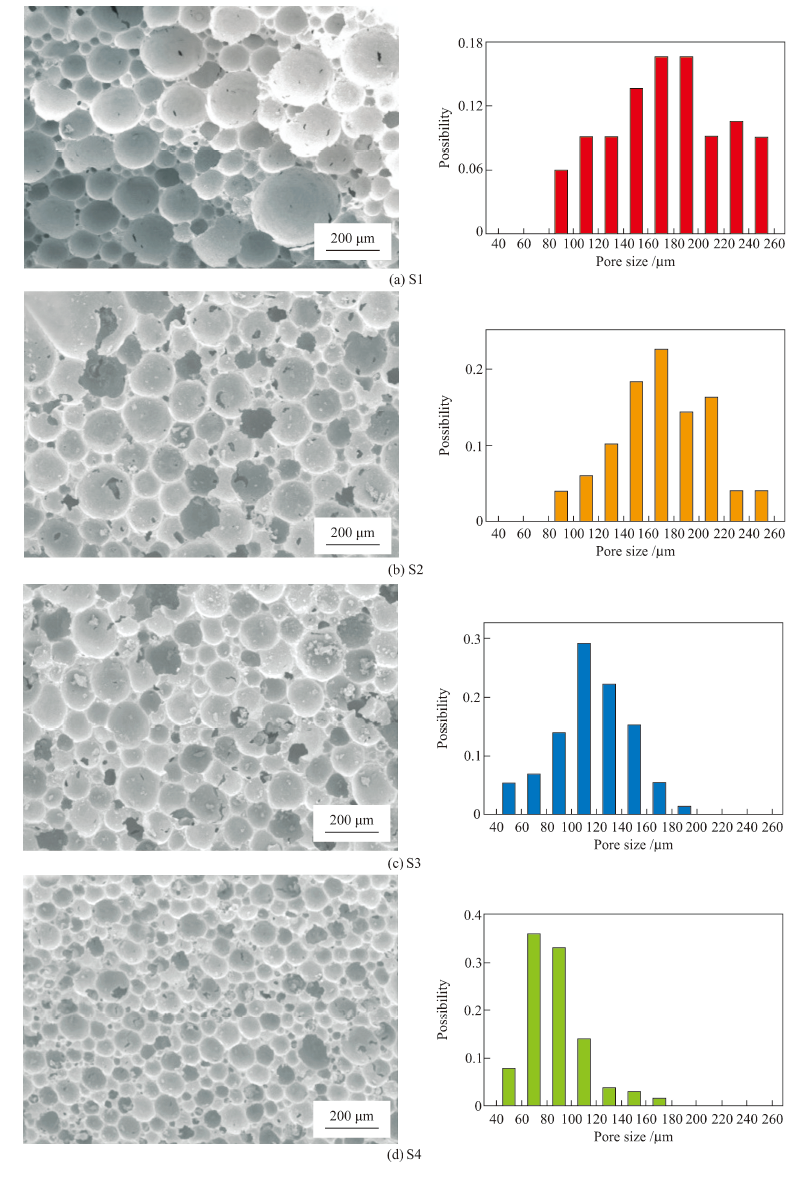
| Samples | Mixed surfactants addition /mass % | Pore size distribution /μm | Average pore size /μm |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 0.1 | 110-275 | 190 |
| S2 | 0.2 | 90-265 | 181 |
| S3 | 0.3 | 55-185 | 126 |
| S4 | 0.4 | 51-175 | 97 |
Table 2 Relationship of mixed surfactants addition and pore size of samples
| Samples | Mixed surfactants addition /mass % | Pore size distribution /μm | Average pore size /μm |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 0.1 | 110-275 | 190 |
| S2 | 0.2 | 90-265 | 181 |
| S3 | 0.3 | 55-185 | 126 |
| S4 | 0.4 | 51-175 | 97 |
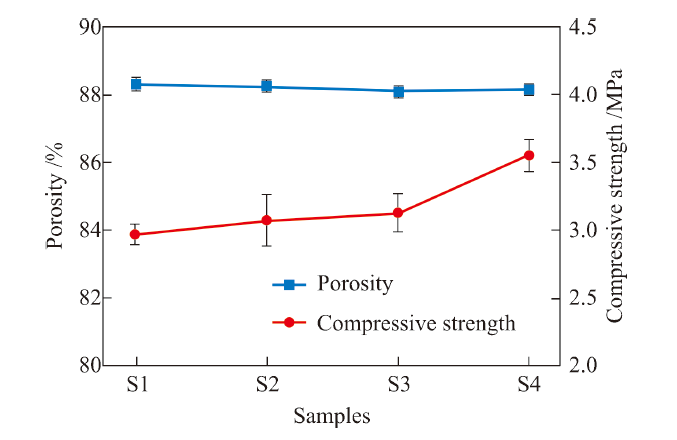
| Samples | Porosity / % | Average pore size /μm | Thermal conductivity / (W · m-1 · K-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 88.31 | 190 | 0.104 |
| S2 | 88.25 | 181 | 0.096 |
| S3 | 88.10 | 126 | 0.093 |
| S4 | 88.15 | 97 | 0.089 |
Table 3 Thermal conductivity of silica ceramic foams with different pore sizes
| Samples | Porosity / % | Average pore size /μm | Thermal conductivity / (W · m-1 · K-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 88.31 | 190 | 0.104 |
| S2 | 88.25 | 181 | 0.096 |
| S3 | 88.10 | 126 | 0.093 |
| S4 | 88.15 | 97 | 0.089 |
| [1] | André R. Studart, Urs T Gonzenbach, Elena Tervoort, Ludwig J Gauckler. Processing routes to macroporous ceramics: A review. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2006, 89(6): 1771-1789. |
| [2] | Wan Tao, Yao Dongxu, Yin Jinwei, Xia Yongfeng, Zuo Kaihui, Liang Hanqin, Zeng Yuping. A novel method for preparing Si3N4 ceramics with unidirectional oriented pores from silicon aqueous slurries. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2017, 37(10): 3285-3291. |
| [3] | T Ohji, M Fukushima. Macro-porous ceramics: Processing and properties. International Materials Reviews, 2012, 57(2): 115-131. |
| [4] | Juanli Yu, Jinlong Yang, Sen Li, Hexin Li, Yong Huang. Preparation of Si3N4 foam ceramics with nest-like cell structure by particle-stabilized foams. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2012, 95(4): 1229-1233. |
| [5] | Dongxu Yao, Yongfeng Xia, Kaihui Zuo, Dongliang Jiang, Jens Günster, Yu-Ping Zeng, Jürgen G Heinrich. The effect of fabrication parameters on the mechanical properties of sintered reaction bonded porous Si3N4 ceramics. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2014, 34(15): 3461-3467. |
| [6] | Wen-Long Huo, Xiao-Yan Zhang, Yu-Gu Chen, Yu-Ju Lu, Wen-Ting Liu, Xiao-Qing Xi, Ya-Li Wang, Jie Xu, Jin-Long Yang. Highly porous zirconia ceramic foams with low thermal conductivity from particle-stabilized foams. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2016, 99(11): 3512-3515. |
| [7] | Zhiqiang Sun, Chen Lu, Junmei Fan, Fangli Yuan. Porous silica ceramics with closed-cell structure prepared by inactive hollow spheres for heat insulation. Journal of Alloys & Compounds, 2016, 662: 157-164. |
| [8] | M. Dresler, S. Reinsch, R. Schadrack, S. Benemann. Burnout behavior of ceramic coated open cell polyurethane (pu) sponges. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2009, 29(16): 3333-3339. |
| [9] | Xiumin Yao, Yong Yang, Xuejian Liu, Zhengren Huang. Effect of recoating slurry compositions on the microstructure and properties of SiC reticulated porous ceramics. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2013, 33(15-16): 2909-2914. |
| [10] | Ali Alem, Martin D. Pugh, Robin A. L. Drew. Open-cell reaction bonded silicon nitride foams: Fabrication and characterization. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2014, 34(3): 599-609. |
| [11] | Yongfeng Xia, Yu-Ping Zeng, Dongliang Jiang. Mechanical and dielectric properties of porous Si3N4 ceramics using pmma as pore former. Ceramics International, 2011, 37(8): 3775-3779. |
| [12] | Liyuan Zhang, Dali Zhou, Ying Chen, Bin Liang, Jiabei Zhou. Preparation of high open porosity ceramic foams via direct foaming molded and dried at room temperature. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2014, 34(10): 2443-2452. |
| [13] | Rizwan Ahmad, Jang-Hoon Ha, In-Hyuck Song. Particle-stabilized ultra-low density zirconia toughened alumina foams. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2013, 33(13-14): 2559-2564. |
| [14] | Manabu Fukushima, Masayuki Nakata, You Zhou, Tatsuki Ohji, Yu-ichi Yoshizawa. Fabrication and properties of ultra highly porous silicon carbide by the gelation-freezing method. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2010, 30(14): 2889-2896. |
| [15] | Xiaojian Mao, Shiwei Wang, Shunzo Shimai. Porous ceramics with tri-modal pores prepared by foaming and starch consolidation. Ceramics International, 2008, 34(1): 107-112. |
| [16] | Xiao-Yan Zhang, Tian Lan, Na Li, Jia-Min Wu, Wen-Long Huo, Ning Ma, Jin-Long Yang. Porous silica ceramics with uniform pores from the in-situ foaming process of silica poly-hollow microspheres in inert atmosphere. Materials Letters, 2016, 182: 143-146. |
| [17] | Takahiro Tomita, Shinji Kawasaki, Kiyoshi Okada. A novel preparation method for foamed silica ceramics by sol-gel reaction and mechanical foaming. Journal of Porous Materials, 2004, 11(2): 107-115. |
| [18] |
Zhongpei Du, Dongxu Yao, Yongfeng Xia, Kaihui Zuo, Jinwei Yin, Hanqin Liang, Yu-Ping Zeng. Highly porous silica foams prepared via direct foaming with mixed surfactants and their sound absorption characteristics. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(9): 12942-12947.
DOI URL |
| [19] | Urs T Gonzenbach, André R Studart, Elena Tervoort, Ludwij J Gauckler. Tailoring the microstructure of particle-stabilized wet foams. Langmuir, 2007, 23(3): 1025-1032. |
| [20] | Yongfeng Xia, Yu-Ping Zeng, Dongliang Jiang. Microstructure and mechanical properties of porous Si3N4 ceramics prepared by freeze-casting. Materials & Design, 2012, 33: 98-103. |
| [21] | R.M. Spriggs. Expression for effect of porosity on elastic modulus of polycrystalline refractory materials, particularly aluminum oxide. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1961, 44(12): 628-629. |
| [22] | Liuyan Yin, Xingui Zhou, Jinshan Yu, Honglei Wang. Preparation of high porous silicon nitride foams with ultra-thin walls and excellent mechanical performance for heat exchanger application by using a protein foaming method. Ceramics International, 2016, 42(1): 1713-1719. |
| [1] | DU Juan, GUO Huishi, YANG Jialin, LI Wenfeng, GUI Yanghai, ZHAO Zhiqiang, LIU Yingfan. Effects of Al2O3-SiO2 Raw Material Types on Properties of Anorthite Based Insulation Refractories [J]. China's Refractories, 2024, 33(1): 23-27. |
| [2] | JIN Zhishang, SHAN Zhilin, ZHAO Huizhong, YU Jun, ZHANG Han. Effect of Porogenic Agents on Properties of Microporous Mullite Aggregates [J]. China's Refractories, 2023, 32(3): 31-35. |
| [3] | WANG Huan, WANG Zhanmin, FENG Haixia, CAO Yingnan, LIU Jun, XU Yingshun. Effect of H2O2 Addition on Anti-explosion Performance of ρ-Al2O3 Bonded Corundum Castables [J]. China's Refractories, 2023, 32(1): 14-19. |
| [4] | SUN Yang, ZHANG Xiuhua, HU Hao, LIU Xiang, LIU Ying, CHEN Bo. Performance of High Thermal Conductivity Dense Silica Bricks and Their High Thermal Conductivity Mechanism [J]. China's Refractories, 2022, 31(1): 30-34. |
| [5] | HE Jian, LYU Xusheng, ZHANG Jialiang, ZHOU Wei, LI Yin. Application Performance of Microporous Sintered Alumina in Alumina Magnesia Castables for Ladles [J]. China's Refractories, 2020, 29(2): 6-10. |
| [6] | ZHANG Yajing, LI Yile, TAN Lihua. Determination of Thermal Physical Properties [J]. , 2018, 27(2): 13-17. |
| [7] | HE Miaolin*, ZHANG Meijie, HUANG Ao. Research for Optimizing Porosity of Porous Thermal-insulating Materials [J]. , 2018, 27(2): 41-44. |
| [8] | CHEN Ruoyu, LI Yuanbing, XIANG Ruofei, LI Shujing, FAN Xiafei, LI Yawei, SANG Shaobai. Effect of Pyrophyllite Addition on Properties of Lightweight Insulation Refractory Materials [J]. , 2017, 26(3): 38-42. |
| [9] | WANG Tongsheng, LI Yawei, SANG Shaobai. Nickel-catalyzed Construction of Heat Conductive Network in Electrically Calcined Anthracite (ECA) Based Carbon Blocks [J]. , 2017, 26(1): 31-37. |
| [10] | YUAN Lin*,WANG Juntao,TONG Lijin, ZHAO Hongliang, LI Quanyou, CHEN Songlin. Composite Design of Low Thermal Conductivity Mullite Brick for Application to Cement Kiln [J]. , 2016, 25(4): 0-0. |
| [11] | E. LITOVSKY,V. ISSOUPOV,J. KLEIMAN. Optimization of Compressed Ceramics Fiber Insulating Layers [J]. , 2016, 25(1): 13-19. |
| [12] | WANG Gang*,YUAN Bo,WU Haibo, DONG Binbin, HAN Jianshen, CHEN Kuo, LI Hongxia. Preparation and Properties of Alumina Heat Insulation Materials with High Purity [J]. , 2015, 24(4): 18-22. |
| [13] | FU Lyuping*,HUANG Ao,GU Huazhi, ZHANG Meijie, LI Zhengkun, ZHAO Yi. Preparation, Performance and Slag Resistant Mechanism of Low Thermal Conductivity Microporous Corundum [J]. , 2015, 24(4): 23-30. |
| [14] | SUN Xiaofei*,WANG Haimei,YUAN Bo, WANG Gang. High Alumina Fiber Composite SiO2 Based Nanoporous Insulation Boards [J]. , 2015, 24(4): 35-38. |
| [15] | LIN Sen*,YAO Dongxu,XIA Yongfeng, ZUO Kaihui, YIN Jinwei, ZENG Yuping. Influence of Yb2O3-MgO on Mechanical Properties and Thermal Conductivity of Silicon Nitride Ceramics via Gas Pressure Sintering [J]. , 2015, 24(3): 34-39. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||