China's Refractories ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (4): 12-18.DOI: 10.19691/j.cnki.1004-4493.2021.04.003
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of Reinforcement and Copper Chill on LM13/ZrSiO4/C Hybrid Metal Matrix Composites (HMMCS)—An Experimental and Statistical Analysis
Yellampalli Prakash RAVITEJ1, Chikkamaranahalli Boganarasimhaiah MOHAN2, Maravanji Gangadharaiah ANANTHAPRASAD3
- 1) Department of Civil and Construction Engineering, Shanxi Institute of Technology, Yangquan 045000, China
2) School of Materials Science and Engineering, Xi’an University of Architecture and Technology, Xi’an 710043, China
-
Online:2021-12-15Published:2021-12-10 -
About author:Mr. Ravitej Y P is pursuing his Ph.D in Material Science and obtained his M. Tech in Dr. Ambedkar Institute of Technology and BE in Sri Siddhartha Institute of Technology. He carried out his internship and project at National Aerospace Laboratories, Bangalore. He has more than six years of teaching and research experience. His research interests are on composites, simulation studies, grain refinement studies and contact stresses in gears of automobiles.
Cite this article
Yellampalli Prakash RAVITEJ, Chikkamaranahalli Boganarasimhaiah MOHAN, Maravanji Gangadharaiah ANANTHAPRASAD. Effect of Reinforcement and Copper Chill on LM13/ZrSiO4/C Hybrid Metal Matrix Composites (HMMCS)—An Experimental and Statistical Analysis[J]. China's Refractories, 2021, 30(4): 12-18.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.cnref.cn/EN/10.19691/j.cnki.1004-4493.2021.04.003
| Composition | mass% |
|---|---|
| Zirconium dioxide (ZrO2) | 64.80 |
| Silicon dioxide (SiO2) | 32.50 |
| Ferric oxide (Fe2O3) | 0.70 |
| Titanium dioxide (TiO2) | 0.15 |
| Alumina (Al2O3) | 1.20 |
Table 1 Composition of starting ZrSiO4 material
| Composition | mass% |
|---|---|
| Zirconium dioxide (ZrO2) | 64.80 |
| Silicon dioxide (SiO2) | 32.50 |
| Ferric oxide (Fe2O3) | 0.70 |
| Titanium dioxide (TiO2) | 0.15 |
| Alumina (Al2O3) | 1.20 |
| Properties of ZrSiO4 | Values | Properties of carbon | Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| Melting point /ºC | 2 500 | Atomic number | 6 |
| Limit of application /ºC | 1 870 | Molecular weight /(g · mol-1) | 12.011 |
| Mohr’s hardness | 7.5 | Apparent density /(g · cm-3) | 2.25 |
| Density /(g · cm-3) | 4.50-4.70 | Bulk density /(g · cm-3) | 3 |
| Linear expansion coefficient /(μm · m-1 · ºC-1) | 4.5 | Melting point /ºC | 3 600 |
| Fracture toughness /MPa | 5 | Boiling point /ºC | 4 200 |
| Crystal structure | Tetragonal | Surface area /(m3 · g-1) | 7.2 |
Table 2 Properties of ZrSiO4 and carbon
| Properties of ZrSiO4 | Values | Properties of carbon | Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| Melting point /ºC | 2 500 | Atomic number | 6 |
| Limit of application /ºC | 1 870 | Molecular weight /(g · mol-1) | 12.011 |
| Mohr’s hardness | 7.5 | Apparent density /(g · cm-3) | 2.25 |
| Density /(g · cm-3) | 4.50-4.70 | Bulk density /(g · cm-3) | 3 |
| Linear expansion coefficient /(μm · m-1 · ºC-1) | 4.5 | Melting point /ºC | 3 600 |
| Fracture toughness /MPa | 5 | Boiling point /ºC | 4 200 |
| Crystal structure | Tetragonal | Surface area /(m3 · g-1) | 7.2 |
| Composition | mass% |
|---|---|
| Si | 11.8 |
| Cu | 1.2 |
| Mg | 0.9 |
| Ni | 0.9 |
| Fe | 0.3 |
| Zn | 0.2 |
| Ti | 0.02 |
| Pb | 0.02 |
| Sn | 0.005 |
| Mn | 0.4 |
| Al | Balance |
Table 3 Composition of LM13
| Composition | mass% |
|---|---|
| Si | 11.8 |
| Cu | 1.2 |
| Mg | 0.9 |
| Ni | 0.9 |
| Fe | 0.3 |
| Zn | 0.2 |
| Ti | 0.02 |
| Pb | 0.02 |
| Sn | 0.005 |
| Mn | 0.4 |
| Al | Balance |
| Specimen number | Copper chill | LM13 | ZrSiO4 | Carbon | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Copper chill end | 2 600 g (As cast) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | Copper chill end | 3 080 g | 3 mass% | 92.4 g | 3 mass% | 92.4 g |
| 3 | Copper chill end | 3 084 g | 6 mass% | 184.5 g | 3 mass% | 92.52 g |
| 4 | Copper chill end | 3 104 g | 9 mass% | 279.36 g | 3 mass% | 93.12 g |
| 5 | Copper chill end | 3 324 g | 12 mass% | 398.88 g | 3 mass% | 99.72 g |
| 6 | Copper non chill end | 2 600 g (As cast) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 7 | Copper non chill end | 3 080 g | 3 mass% | 92.4 g | 3 mass% | 92.4 g |
| 8 | Copper non chill end | 3 084 g | 6 mass% | 184.5 g | 3 mass% | 92.52 g |
| 9 | Copper non chill end | 3 104 g | 9 mass% | 279.36 g | 3 mass% | 93.12 g |
| 10 | Copper non chill end | 3 324 g | 12 mass% | 398.88 g | 3 mass% | 99.73 g |
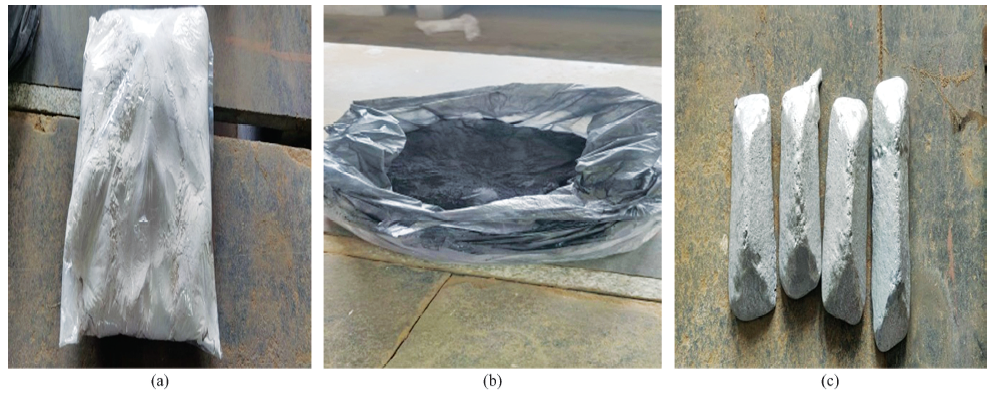
Table 4 Percentages of LM13, ZrSiO4, and carbon used for casting
| Specimen number | Copper chill | LM13 | ZrSiO4 | Carbon | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Copper chill end | 2 600 g (As cast) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | Copper chill end | 3 080 g | 3 mass% | 92.4 g | 3 mass% | 92.4 g |
| 3 | Copper chill end | 3 084 g | 6 mass% | 184.5 g | 3 mass% | 92.52 g |
| 4 | Copper chill end | 3 104 g | 9 mass% | 279.36 g | 3 mass% | 93.12 g |
| 5 | Copper chill end | 3 324 g | 12 mass% | 398.88 g | 3 mass% | 99.72 g |
| 6 | Copper non chill end | 2 600 g (As cast) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 7 | Copper non chill end | 3 080 g | 3 mass% | 92.4 g | 3 mass% | 92.4 g |
| 8 | Copper non chill end | 3 084 g | 6 mass% | 184.5 g | 3 mass% | 92.52 g |
| 9 | Copper non chill end | 3 104 g | 9 mass% | 279.36 g | 3 mass% | 93.12 g |
| 10 | Copper non chill end | 3 324 g | 12 mass% | 398.88 g | 3 mass% | 99.73 g |
| Material of the chill | Density /(g · cm-3) | Specific heat / (J · kg-1 · K-1) | Thermal conductivity / (W · m-1 · K-1) | Volumetric heat capacity for 25 mm chill /(J · K-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | 8. 961 | 0. 449 | 380 | 597. 1 |
| Steel | 7. 850 | 0. 422 | 52 | 491. 51 |
| Cast iron | 7. 62 | 0. 402 | 40 | 453. 91 |
| Silicon carbide | 2. 37 | 1. 096 | 120 | 384. 31 |
Table 5 Thermo physical properties of different chills
| Material of the chill | Density /(g · cm-3) | Specific heat / (J · kg-1 · K-1) | Thermal conductivity / (W · m-1 · K-1) | Volumetric heat capacity for 25 mm chill /(J · K-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | 8. 961 | 0. 449 | 380 | 597. 1 |
| Steel | 7. 850 | 0. 422 | 52 | 491. 51 |
| Cast iron | 7. 62 | 0. 402 | 40 | 453. 91 |
| Silicon carbide | 2. 37 | 1. 096 | 120 | 384. 31 |
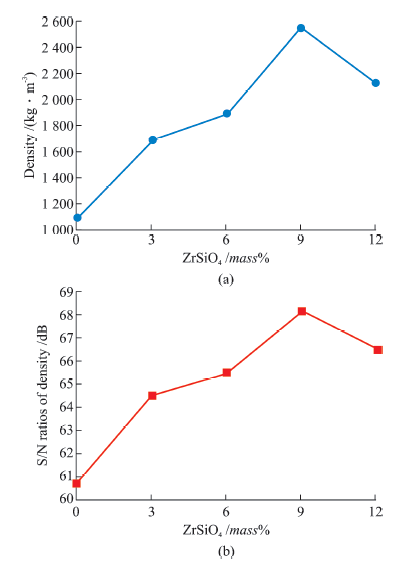
| Specimen No. | Specimen diameter /mm | Initial gauge length /mm | Initial cross sectional area /mm2 | Final gauge length /mm | Load at peak /kN | Percent elongation /% | Density / (kg · m-3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 8.99 | 45 | 63.48 | 45.78 | 104.33 | 1.58 | 2 460.03 |
| 2 | 8.98 | 45 | 63.33 | 45.33 | 119.60 | 0.73 | 2 498.25 |
| 3 | 9.00 | 45 | 63.62 | 45.21 | 124.50 | 0.71 | 2 769.88 |
| 4 | 8.96 | 45 | 63.05 | 45.43 | 145.35 | 0.96 | 2 777.54 |
| 5 | 9.02 | 45 | 63.90 | 46.10 | 134.60 | 2.50 | 2 665.33 |
| 6 | 9.09 | 45 | 63.49 | 45.88 | 101.20 | 1.47 | 1 084.02 |
| 7 | 8.88 | 45 | 63.45 | 45.45 | 101.50 | 0.69 | 1 685.21 |
| 8 | 9.40 | 45 | 63.95 | 45.66 | 103.70 | 0.68 | 1 888.84 |
| 9 | 8.66 | 45 | 63.15 | 45.22 | 121.50 | 0.87 | 2 552.52 |
| 10 | 9.82 | 45 | 63.45 | 46.30 | 107.90 | 2.41 | 2 125.31 |
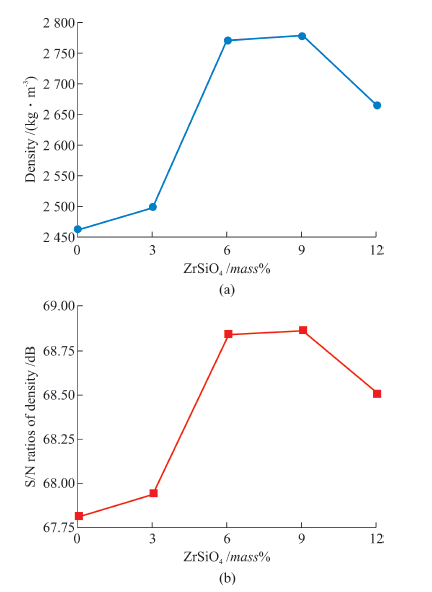
Table 6 Tensile test set up
| Specimen No. | Specimen diameter /mm | Initial gauge length /mm | Initial cross sectional area /mm2 | Final gauge length /mm | Load at peak /kN | Percent elongation /% | Density / (kg · m-3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 8.99 | 45 | 63.48 | 45.78 | 104.33 | 1.58 | 2 460.03 |
| 2 | 8.98 | 45 | 63.33 | 45.33 | 119.60 | 0.73 | 2 498.25 |
| 3 | 9.00 | 45 | 63.62 | 45.21 | 124.50 | 0.71 | 2 769.88 |
| 4 | 8.96 | 45 | 63.05 | 45.43 | 145.35 | 0.96 | 2 777.54 |
| 5 | 9.02 | 45 | 63.90 | 46.10 | 134.60 | 2.50 | 2 665.33 |
| 6 | 9.09 | 45 | 63.49 | 45.88 | 101.20 | 1.47 | 1 084.02 |
| 7 | 8.88 | 45 | 63.45 | 45.45 | 101.50 | 0.69 | 1 685.21 |
| 8 | 9.40 | 45 | 63.95 | 45.66 | 103.70 | 0.68 | 1 888.84 |
| 9 | 8.66 | 45 | 63.15 | 45.22 | 121.50 | 0.87 | 2 552.52 |
| 10 | 9.82 | 45 | 63.45 | 46.30 | 107.90 | 2.41 | 2 125.31 |
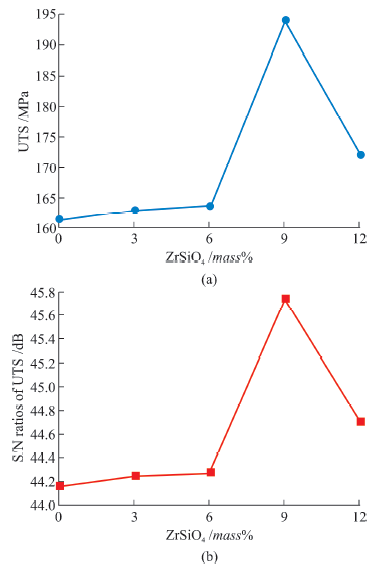
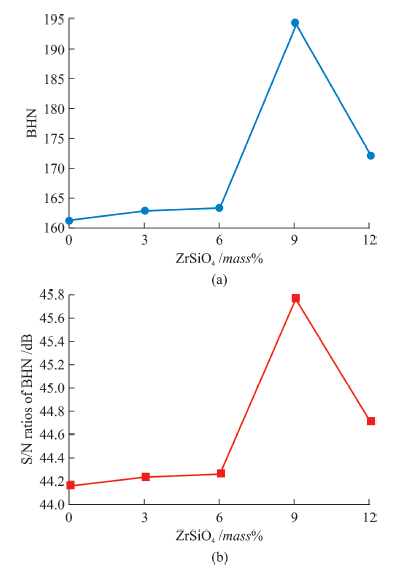
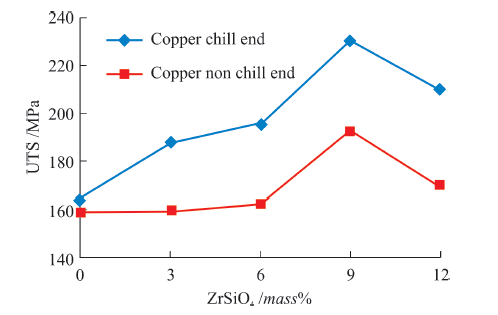
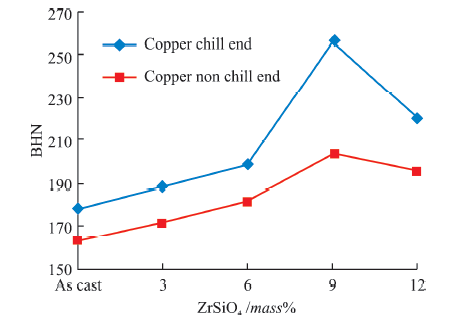
| Specimen No. | UTS numerical /MPa | UTS experimental /MPa | UTS difference /MPa | UTS S/N ratio /dB | Hardness S/N ratio /dB | Density S/N ratio /dB | BHN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 164.36 | 165.26 | 0.90 | 44.31 | 44.4 | 67.82 | 178.52 |
| 2 | 188.86 | 189.65 | 0.79 | 45.52 | 45.6 | 67.95 | 188.43 |
| 3 | 195.70 | 196.69 | 0.99 | 45.83 | 45.8 | 68.85 | 197.73 |
| 4 | 230.54 | 232.30 | 1.76 | 47.25 | 47.3 | 68.87 | 255.9 |
| 5 | 210.65 | 212.00 | 1.35 | 46.47 | 46.6 | 68.52 | 220.9 |
| 6 | 159.44 | 161.32 | 1.88 | 44.15 | 45.0 | 60.70 | 164.08 |
| 7 | 160.00 | 162.98 | 2.98 | 44.24 | 45.6 | 64.53 | 172.3 |
| 8 | 162.20 | 163.45 | 1.25 | 44.27 | 45.9 | 65.52 | 182.09 |
| 9 | 192.54 | 194.02 | 1.48 | 45.76 | 48.2 | 68.14 | 204.35 |
| 10 | 170.20 | 172.05 | 1.85 | 44.15 | 47.2 | 66.55 | 195.43 |
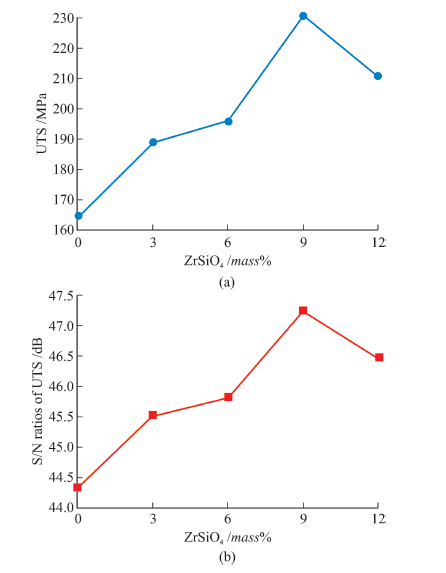
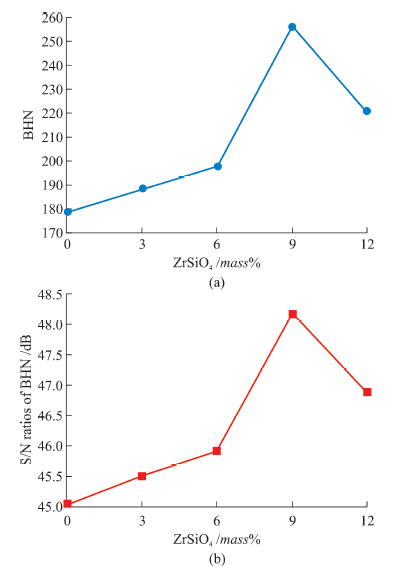
Table 7 Tensile test results
| Specimen No. | UTS numerical /MPa | UTS experimental /MPa | UTS difference /MPa | UTS S/N ratio /dB | Hardness S/N ratio /dB | Density S/N ratio /dB | BHN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 164.36 | 165.26 | 0.90 | 44.31 | 44.4 | 67.82 | 178.52 |
| 2 | 188.86 | 189.65 | 0.79 | 45.52 | 45.6 | 67.95 | 188.43 |
| 3 | 195.70 | 196.69 | 0.99 | 45.83 | 45.8 | 68.85 | 197.73 |
| 4 | 230.54 | 232.30 | 1.76 | 47.25 | 47.3 | 68.87 | 255.9 |
| 5 | 210.65 | 212.00 | 1.35 | 46.47 | 46.6 | 68.52 | 220.9 |
| 6 | 159.44 | 161.32 | 1.88 | 44.15 | 45.0 | 60.70 | 164.08 |
| 7 | 160.00 | 162.98 | 2.98 | 44.24 | 45.6 | 64.53 | 172.3 |
| 8 | 162.20 | 163.45 | 1.25 | 44.27 | 45.9 | 65.52 | 182.09 |
| 9 | 192.54 | 194.02 | 1.48 | 45.76 | 48.2 | 68.14 | 204.35 |
| 10 | 170.20 | 172.05 | 1.85 | 44.15 | 47.2 | 66.55 | 195.43 |
| [1] | J. K. Chaurasia, P. Patel, M. Muthuchamy. Investigation of zirconium silicate and zirconium oxide reinforcement in aluminium 6061 metal matrix : A Comparative Study. 2016. |
| [2] | K. S. Sucitharan. Wear behaviour of Al6063-zircon sand metal matrix composite. IOSR Journal of Engineering, 2013,3(2):24-28. |
| [3] | Abhilash B. Mhaske, Prof. K, R. Madavi., . Experimental investigation and optimization of wear properties of aluminum alloy LM30 composite with zircon powder as reinforcement. International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET), 2018(7):2062-2065. |
| [4] | SN Kumar, YP Ravitej, H Adarsha, BS Halemani, M Veeracahri. Fabrication and characterization of hardness and microstructure of large sized Al2014-SiC composite. Materials Today: Proceedings, 2021,46(18):9102-9106. |
| [5] | R. Prem chand, Y. P. Ravitej, K. M. Chandrasekhar, H. Adarsha, J. V. Shivamani kanta, M. Veerachari, R. Ravi kumar, Abhinandan. Characterization of banana and E glass fiber reinforced hybrid epoxy composites. Materials Today: Proceedings, 2021,46(18):9119-9125. |
| [6] | V. Deepak, O. Abhilash, Y. P. Ravitej, Veerachari, L. Abhinandan. Design and development of progressive tool for mold tag. AIP Conference Proceedings 2021,2316:030015. |
| [7] | D Sandeep, Y P Ravitej, Sachin Khot, R Ravikumar, Sandeep,. CFD simulation of transonic turbulent flow past NACA 0012 aerofoil. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2021,2316:20013. |
| [8] | Y. P. Ravitej, V. Swaroop, S. Ramesh, H. Adarsha, Veerachari, Nischith. Finite element analysis of mild steel - Rubber sandwich composite material. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 2018,376(1):012040. |
| [9] | Ravitej Y P, Ramesh S, Syed Sameer, Vedavathi Banda, Veerachari M. Bending stresses and wear reduction in an involute spur gear. International Journal of Advanced Research Trends in Engineering and Technology (IJARTET), 2018(5):432-436. |
| [10] | Jenix Rino, Sivalingappa, Halesh Koti, V Daniel Jebin. Properties of Al6063 MMC reinforced with zircon sand and alumina. IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering, 2013,5(5):72-77. |
| [11] | Syed Ahamed, Roshan J D, Shilpa P C. Evolution of tensile and fracture toughness properties of aluminum-7075 alloy reinforced with zirconium silicate (ZrSiO4) particulates. International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET), 2019(6):1314-1320. |
| [12] | B. G. Jayaraja, P. Mathivanan, M. J. Monish. Testing and analysis of mechanical properties of Al-ZrSiO4 C-Hybrid nano composites. International Journal for Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology (IJRASET), 2018(4):27-32. |
| [13] | R. Nateriya, S. K. Patel, G. Dixit. Microstructural and erosive wear behavior on coarse silica sand of dual reinforced particle (DRP) LM-13 alloy composites. Materials Today: Proceedings, 2017,4(2):3431-3440. |
| [14] | J. Hemanth. Development and property evaluation of aluminum alloy reinforced with nano-ZrO2 metal matrix composites (NMMCs). Materials Science and Engineering A, 2009,507(1):110-113. |
| [15] | Nityanand Bandekar, M. G. Anantha Prasad. Mechanical and wear behavior of aluminum-garnet carbon chill cast hybrid composites. Indian Journal of Science and Technology, 2019(12):1-8. |
| [1] | WANG Zhanmin*,ZHAO Jin,CAO Xiying, YU Lingyan, ZHANG Sanhua, SHI Gan, HUANG Yufei, ZHU Zhu. Study on Mechanism of Explosive Spalling of ULC Castables During Rapid Drying [J]. , 2015, 24(4): 1-6. |
| [2] | XU Jianfeng,FU Shunde,LIU Libin, JIA Jia, GAN Xiaoming. Influence of Heating Rate and Calcining Temperature on Properties of 95 Polycrystalline Alumina Fiber [J]. China's Refractories, 2012, 21(3): -. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||