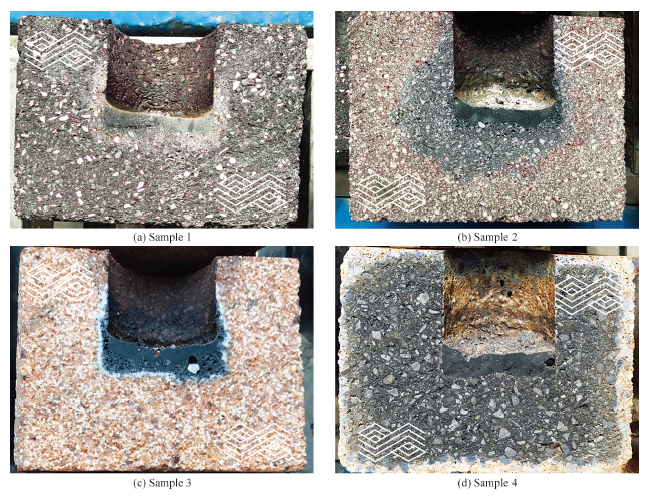
China's Refractories ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (2): 12-15.DOI: 10.19691/j.cnki.1004-4493.2021.02.003
• Original article • Previous Articles Next Articles
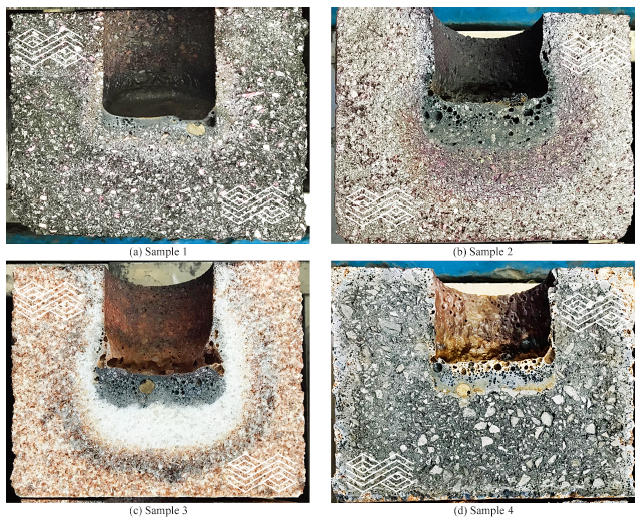
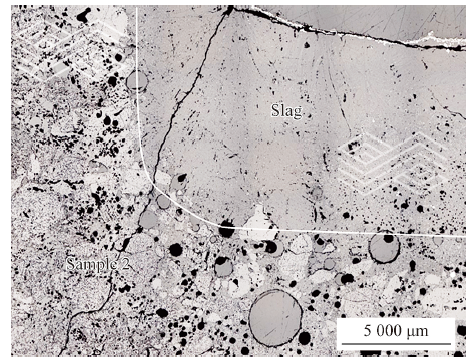
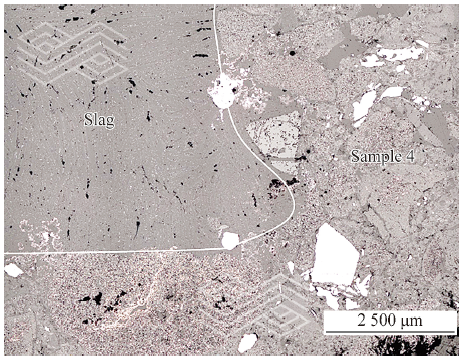
Corrosion-resistant Refractory Linings for Hazardous Waste Treatment in Rotary Kilns
Chongchong NIU1,*( ), Christina STIMPFL2, Danting ZHAO1
), Christina STIMPFL2, Danting ZHAO1
- 1 RHI Magnesita, Dalian 116600, China
2 RHI Magnesita, Shanghai 200021, China